Sequence-specific binding of single-stranded RNA: is there a code for recognition?
- PMID: 16982642
- PMCID: PMC1635273
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl620
Sequence-specific binding of single-stranded RNA: is there a code for recognition?
Abstract
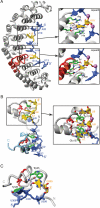
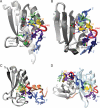
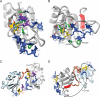
A code predicting the RNA sequence that will be bound by a certain protein based on its amino acid sequence or its structure would provide a useful tool for the design of RNA binders with desired sequence-specificity. Such de novo designed RNA binders could be of extraordinary use in both medical and basic research applications. Furthermore, a code could help to predict the cellular functions of RNA-binding proteins that have not yet been extensively studied. A comparative analysis of Pumilio homology domains, zinc-containing RNA binders, hnRNP K homology domains and RNA recognition motifs is performed in this review. Based on this, a set of binding rules is proposed that hints towards a code for RNA recognition by these domains. Furthermore, we discuss the intermolecular interactions that are important for RNA binding and summarize their importance in providing affinity and specificity.
Figures
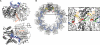

References
-
- Klug A. Towards therapeutic applications of engineered zinc finger proteins. FEBS Lett. 2005;579:892–894. - PubMed
-
- Messias A.C., Sattler M. Structural basis of single-stranded RNA recognition. Acc. Chem. Res. 2004;37:279–287. - PubMed
-
- Spassov D.S., Jurecic R. The PUF family of RNA-binding proteins: does evolutionarily conserved structure equal conserved function? IUBMB Life. 2003;55:359–366. - PubMed
-
- de Moor C.H., Meijer H., Lissenden S. Mechanisms of translational control by the 3′ UTR in development and differentiation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005;16:49–58. - PubMed
-
- Wang X., McLachlan J., Zamore P.D., Hall T.M. Modular recognition of RNA by a human pumilio-homology domain. Cell. 2002;110:501–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

