Cell biology of membrane trafficking in human disease
- PMID: 16984815
- PMCID: PMC7112332
- DOI: 10.1016/S0074-7696(06)52005-4
Cell biology of membrane trafficking in human disease
Abstract
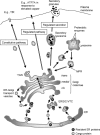
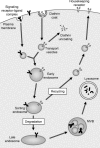
Understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying membrane traffic pathways is crucial to the treatment and cure of human disease. Various human diseases caused by changes in cellular homeostasis arise through a single gene mutation(s) resulting in compromised membrane trafficking. Many pathogenic agents such as viruses, bacteria, or parasites have evolved mechanisms to subvert the host cell response to infection, or have hijacked cellular mechanisms to proliferate and ensure pathogen survival. Understanding the consequence of genetic mutations or pathogenic infection on membrane traffic has also enabled greater understanding of the interactions between organisms and the surrounding environment. This review focuses on human genetic defects and molecular mechanisms that underlie eukaryote exocytosis and endocytosis and current and future prospects for alleviation of a variety of human diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Aldred M.A., Ginn‐Pease M.E., Morrison C.D., Popkie A.P., Gimm O., Hoang‐Vu C., Krause U., Dralle H., Jhiang S.M., Plass C., Eng C. Caveolin‐1 and caveolin‐2,together with three bone morphogenetic protein‐related genes, may encode novel tumor suppressors down‐regulated in sporadic follicular thyroid carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2003;63:2864–2871. - PubMed
-
- Al‐Hasani H., Hinck C.S., Cushman S.W. Endocytosis of the glucose transporter GLUT4 is mediated by the GTPase dynamin. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:17504–17510. - PubMed
-
- Allan V.J., Thompson H.M., McNiven M.A. Motoring around the Golgi. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002;4:E236. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez C., Garcia‐Mata R., Hauri H.‐P., Sztul E. The p115‐interactive proteins GM130 and giantin participate in endoplasmic reticulum‐Golgi traffic. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:2693–2700. - PubMed
-
- Amaral M.D. CFTR and chaperones: Processing and degradation. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2004;23:41–48. - PubMed
Further Reading
-
- Cox D.W., Moore S.D. Copper transporting P‐type ATPases and human disease. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2002;34:333–338. - PubMed
-
- Gitlin J.D. Wilson disease. Gastroenterology. 2003;125:1868–1877. - PubMed
-
- Robinson M.S., Römisch K. Surfing the Sec61 channel: Bidirectional protein translocation across the ER membrane. J. Cell Sci. 1999;112(Pt. 23):4185–4191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

