The bipartite architecture of the sRNA in an archaeal box C/D complex is a primary determinant of specificity
- PMID: 16984968
- PMCID: PMC1635284
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl644
The bipartite architecture of the sRNA in an archaeal box C/D complex is a primary determinant of specificity
Abstract
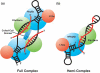
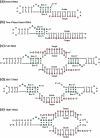
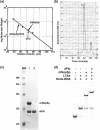
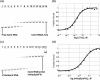
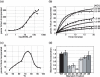
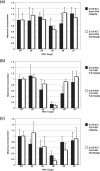
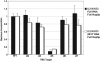
The archaeal box C/D sRNP, the enzyme responsible for 2'-O-methylation of rRNA and tRNA, possesses a nearly perfect axis of symmetry and bipartite structure. This RNP contains two platforms for the assembly of protein factors, the C/D and C'/D' motifs, acting in conjunction with two guide sequences to direct methylation of a specific 2'-hydroxyl group in a target RNA. While this suggests that a functional asymmetric single-site complex complete with guide sequence and a single box C/D motif should be possible, previous work has demonstrated such constructs are not viable. To understand the basis for a bipartite RNP, we have designed and assayed the activity and specificity of a series of synthetic RNPs that represent a systematic reduction of the wild-type RNP to a fully single-site enzyme. This reduced RNP is active and exhibits all of the characteristics of wild-type box C/D RNPs except it is nonspecific with respect to the site of 2'-O-methylation. Our results demonstrate that protein-protein crosstalk through Nop5p dimerization is not required, but that architecture plays a crucial role in directing methylation activity with both C/D and C'/D' motifs being required for specificity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conserved spacing between the box C/D and C'/D' RNPs of the archaeal box C/D sRNP complex is required for efficient 2'-O-methylation of target RNAs.RNA. 2005 Mar;11(3):285-93. doi: 10.1261/rna.7223405. Epub 2005 Jan 20. RNA. 2005. PMID: 15661846 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient RNA 2'-O-methylation requires juxtaposed and symmetrically assembled archaeal box C/D and C'/D' RNPs.EMBO J. 2003 Aug 1;22(15):3930-40. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg368. EMBO J. 2003. PMID: 12881427 Free PMC article.
-
Functional requirement for symmetric assembly of archaeal box C/D small ribonucleoprotein particles.J Mol Biol. 2003 Oct 17;333(2):295-306. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2003.08.012. J Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 14529617
-
RNA structure and function in C/D and H/ACA s(no)RNPs.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004 Jun;14(3):335-43. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.05.006. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004. PMID: 15193314 Review.
-
The structure and function of small nucleolar ribonucleoproteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(5):1452-64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl1172. Epub 2007 Feb 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17284456 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis for site-specific ribose methylation by box C/D RNA protein complexes.Nature. 2011 Jan 27;469(7331):559-63. doi: 10.1038/nature09688. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21270896
-
The box C/D sRNP dimeric architecture is conserved across domain Archaea.RNA. 2012 Aug;18(8):1527-40. doi: 10.1261/rna.033134.112. Epub 2012 Jun 29. RNA. 2012. PMID: 22753779 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of a critical interaction within the archaeal box C/D small ribonucleoprotein complex.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 29;284(22):15317-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M901368200. Epub 2009 Mar 31. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19336398 Free PMC article.
-
Archaeal fibrillarin-Nop5 heterodimer 2'-O-methylates RNA independently of the C/D guide RNP particle.RNA. 2017 Sep;23(9):1329-1337. doi: 10.1261/rna.059832.116. Epub 2017 Jun 2. RNA. 2017. PMID: 28576826 Free PMC article.
-
Programmable sequence-specific click-labeling of RNA using archaeal box C/D RNP methyltransferases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Aug;40(14):6765-73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks381. Epub 2012 May 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22564896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ziesche S.M., Omer A.D., Dennis P.P. RNA-guided nucleotide modification of ribosomal and non-ribosomal RNAs in Archaea. Mol. Microbiol. 2004;54:980–993. - PubMed
-
- Clouet-d'Orval B., Gaspin C., Mougin A. Two different mechanisms for tRNA ribose methylation in Archaea: a short survey. Biochimie. 2005;87:889–895. - PubMed
-
- Decatur W.A., Fournier M.J. RNA-guided nucleotide modification of ribosomal and other RNAs. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:695–698. - PubMed

