CTD kinase I is required for the integrity of the rDNA tandem array
- PMID: 16984969
- PMCID: PMC1635248
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl493
CTD kinase I is required for the integrity of the rDNA tandem array
Abstract
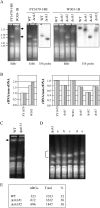
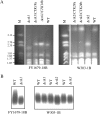
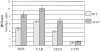
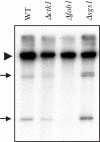
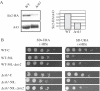
The genomic stability of the rDNA tandem array is tightly controlled to allow sequence homogenization and to prevent deleterious rearrangements. In this report, we show that the absence of the yeast CTD kinase I (CTDK-I) complex in null mutant strains leads to a decrease in the number of tandem rDNA repeats. Reintroduction of the missing gene induces an increase of rDNA repeats to reach a copy number similar to that of the original strain. Interestingly, while expansion is dependent on Fob1, a protein required for replication fork blocking activity in rDNA, contraction occurs in the absence of Fob1. Furthermore, silencing of class II genes at the rDNA, a process connected to rDNA stability, is not affected. Ctk1, the kinase subunit of the CTDK-I complex is involved in various steps of mRNA synthesis. In addition, we have recently shown that Ctk1 is also implicated in rRNA synthesis. The results suggest that the RNA polymerase I transcription defect occurring in a ctk1 mutant strain causes rDNA contraction.
Figures

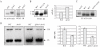
Similar articles
-
Association of the RENT complex with nontranscribed and coding regions of rDNA and a regional requirement for the replication fork block protein Fob1 in rDNA silencing.Genes Dev. 2003 Sep 1;17(17):2162-76. doi: 10.1101/gad.1108403. Epub 2003 Aug 15. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 12923057 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion and contraction of ribosomal DNA repeats in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: requirement of replication fork blocking (Fob1) protein and the role of RNA polymerase I.Genes Dev. 1998 Dec 15;12(24):3821-30. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.24.3821. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9869636 Free PMC article.
-
Replication fork arrest and rDNA silencing are two independent and separable functions of the replication terminator protein Fob1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 23;285(17):12612-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.082388. Epub 2010 Feb 23. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20179323 Free PMC article.
-
[Recombination regulation by noncoding transcription in yeast rDNA repeats].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2006 Nov;51(14 Suppl):2141-3. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2006. PMID: 17471925 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Ribosomal DNA stability is supported by many 'buffer genes'-introduction to the Yeast rDNA Stability Database.FEMS Yeast Res. 2017 Jan 1;17(1). doi: 10.1093/femsyr/fox001. FEMS Yeast Res. 2017. PMID: 28087673 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative genome-wide screening identifies a conserved doxorubicin repair network that is diploid specific in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.PLoS One. 2009 Jun 8;4(6):e5830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005830. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19503795 Free PMC article.
-
Ctk1 function is necessary for full translation initiation activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Eukaryot Cell. 2015 Jan;14(1):86-95. doi: 10.1128/EC.00106-14. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Eukaryot Cell. 2015. PMID: 25416238 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinases: Masters of the eukaryotic universe.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Sep 17;15(1):e1816. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1816. Online ahead of print. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 37718413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CDK12 is a transcription elongation-associated CTD kinase, the metazoan ortholog of yeast Ctk1.Genes Dev. 2010 Oct 15;24(20):2303-16. doi: 10.1101/gad.1968210. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20952539 Free PMC article.
-
RNAP-II molecules participate in the anchoring of the ORC to rDNA replication origins.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53405. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053405. Epub 2013 Jan 4. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23308214 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

