Distinct memory CD4+ T-cell subsets mediate immune recognition of Epstein Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 in healthy virus carriers
- PMID: 16985171
- PMCID: PMC1785143
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-05-023663
Distinct memory CD4+ T-cell subsets mediate immune recognition of Epstein Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 in healthy virus carriers
Abstract
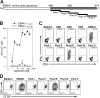
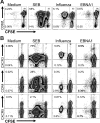
CD4+ T cells, specific for transforming latent infection with the Epstein Barr virus (EBV), consistently recognize the nuclear antigen 1 of EBV (EBNA1). EBNA1-specific effector CD4+ T cells are primarily T-helper 1 (TH1) polarized. Here we show that most healthy EBV carriers have such IFN-secreting EBNA1-specific CD4+ T cells at a frequency of 0.03% of circulating CD4+ T cells. In addition, healthy carriers have a large pool of CD4+ T cells that proliferated in response to EBNA1 and consisted of distinct memory-cell subsets. Despite continuous antigen presence due to persistent EBV infection, half of the proliferating EBNA1-specific CD4+ T cells belonged to the central-memory compartment (TCM). The remaining EBNA1-specific CD4+ T cells displayed an effector-memory phenotype (TEM), of which a minority rapidly secreted IFN upon stimulation with EBNA1. Based on chemokine receptor analysis, all EBNA1-specific TCM CD4+ T cells were TH1 committed. Our results suggest that protective immune control of chronic infections, like EBV, includes a substantial reservoir of TCM CD4+ TH1 precursors, which continuously fuels TH1-polarized effector cells.
Figures




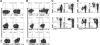
References
-
- Chan AT, Teo PM, Johnson PJ. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann Oncol. 2002;13:1007–1015. - PubMed
-
- Macsween KF, Crawford DH. Epstein-Barr virus-recent advances. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3:131–140. - PubMed
-
- Nalesnik MA. Clinicopathologic characteristics of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2002;159:9–18. - PubMed
-
- Bar RS, DeLor CJ, Clausen KP, Hurtubise P, Henle W, Hewetson JF. Fatal infectious mononucleosis in a family. N Engl J Med. 1974;290:363–367. - PubMed
-
- Purtilo DT, Cassel C, Yang JP. Letter: Fatal infectious mononucleosis in familial lymphohistiocytosis. N Engl J Med. 1974;291:736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

