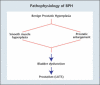
Pathophysiology, epidemiology, and natural history of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- PMID: 16985922
- PMCID: PMC1472917
Pathophysiology, epidemiology, and natural history of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Abstract
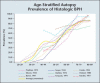
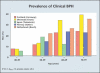
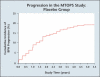
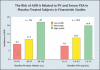
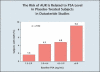
The pathophysiology, epidemiology, and natural history of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) are incompletely understood; however, the development of reliable instruments to measure symptom severity, prostatic enlargement, and bladder outlet obstruction has allowed major advances in their elucidation. The development of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in the aging male is influenced to some degree by the severity of bladder outlet obstruction and prostatic enlargement. Although the development of LUTS, bladder outlet obstruction, and BPH are age-dependent, they are not necessarily causally related; there are many other factors involved in the pathophysiology of LUTS. The clinically important parameters of disease progression in men with moderate to severe LUTS and low peak flow rates are symptom progression and the development of acute urinary retention (AUR). The risk of AUR is related to both baseline serum prostate-specific antigen level and prostate volume. In men with moderate prostate enlargement, the risk of AUR appears to be high enough to justify intervention with a 5alpha-reductase inhibitor in order to reduce this risk.
Figures
References
-
- McNeal JG. The prostate gland: morphology and pathobiology. Monogr Urol. 1983;4:3–33.
-
- Jepsen JV, Bruskewitz RC. Clinical manifestation and indications for treatment. In: Lepor H, editor. Prostatic Diseases. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders Co; 2000. pp. 123–142.
-
- Berry SJ, Coffey DS, Walsh PC, et al. The development of human prostatic hyperplasia with age. J Urol. 1984;132:474–479. - PubMed
-
- Roehrborn CG, McConnell JD. Etiology, pathophysiology, epidemiology and natural history of benign prostatic hyperplasia. In: Walsh PC, Retik AB, Vaughan ED Jr, Wein AJ, editors. Campbell’s Urology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders Co; 2002. pp. 1297–1336.
-
- McConnell JD. Prostatic growth: new insights into hormonal regulation. Br J Urol. 1995;76(suppl 1):5–10. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
