Complementary and alternative therapies as treatment approaches for interstitial cystitis
- PMID: 16986031
- PMCID: PMC1476005
Complementary and alternative therapies as treatment approaches for interstitial cystitis
Abstract
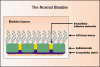
The management of interstitial cystitis (IC) is predominantly the reduction of the symptoms of frequency, urgency, and pain. Multimodal treatment approaches for IC are helpful in customizing therapy for individual patients. Complementary and alternative therapies are a quintessential addition to the therapeutic armamentarium and frequently include dietary modification, nutraceuticals, bladder training, neuromodulation, stress reduction, and sex therapy. Dietary modification involves elimination of bladder irritants, fluid regulation, and a bowel regimen. Nutraceuticals studied for the treatment of IC include calcium glycerophosphate, L-arginine, mucopolysaccharides, bioflavinoids, and Chinese herbs. Bladder training is effective after pain reduction. The neuromodulation of high-tone pelvic-floor muscle dysfunction is achieved with physical therapy and acupuncture. Stress reduction and sex therapy are best administered by a qualified stress manager and sex therapist. Multimodal, nonconventional management may add efficacy to the treatment of IC.
Figures

References
-
- Ernst E, Resch KI, Mills S, et al. Complementary medicine: a definition. Br J Gen Prac. 1995;45:506–509.
-
- Hirsch I. Integrative urology: a spectrum of complementary and alternative therapy. Urology. 2000;56:185–189. - PubMed
-
- Whitmore KE. Self-care regimens for patients with interstitial cystitis. Urol Clin North Am. 1994;21:121–130. - PubMed
-
- Koziol JA, Clark DC, Gittes RF, et al. The natural history of interstitial cystitis: a survey of 374 patients. J Urol. 1993;149:465–469. - PubMed
-
- Gillespie L. Metabolic appraisal of the effects of dietary modification on hypersensitive bladder symptoms. Br J Urol. 1993;72:293–297. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
