Optimization of cutaneous electrically mediated plasmid DNA delivery using novel electrode
- PMID: 16988718
- PMCID: PMC3266623
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302867
Optimization of cutaneous electrically mediated plasmid DNA delivery using novel electrode
Abstract
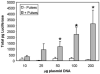
The easy accessibility of skin makes it an excellent target for gene transfer protocols. To take advantage of skin as a target for gene transfer, it is important to establish an efficient and reproducible delivery system. Electroporation is an established technique for enhancing plasmid delivery to many tissues in vivo. A critical component of this technique is the electrode configuration. Electroporation parameters were optimized for transgene expression with minimal tissue damage with a novel electrode. The highest transgene expression and efficiency of individual cell transformation with minimal damage was produced with eight 150 ms pulses at field strength of 100 V/cm. This electrode design offers the potential for easier and more reproducible electrically mediated cutaneous plasmid delivery than the simple electrodes currently commercially available. This electrode can be a valuable tool in determining the applicability of electrically mediated cutaneous gene transfer.
Figures




References
-
- Titomirov AV, Sukharev S, Kistanova E. In vivo electroporation and stable transformation of skin cells of newborn mice by plasmid DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1088:131–134. - PubMed
-
- Drabick JJ, Glasspool-Malone J, Somiari S, King A, Malone RW. Cutaneous transfection and immune responses to intradermal nucleic acid vaccination are significantly enhanced by in vivo electroporation. Mol Ther. 2000;3:249–255. - PubMed
-
- Glasspool-Malone J, Somiara S, Drabick JJ, Malone RW. Efficient nonviral cutaneous transfection. Mol Ther. 2000;2:140–146. - PubMed
-
- Chesnoy S, Huang L. Enhanced cutaneous gene delivery following intradermal injection of naked DNA in a high ionic strength solution. Mol Ther. 2001;5:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Maruyama H, Ataka K, Higuchi N, Sakamoto F, Gejyo F, Miyazaki J. Skin-targeted gene transfer using in vivo electroporation. Gene Therapy. 2001;8:1808–1812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

