Quantitative comparison of the efficiency of antibodies against S1 and S2 subunit of SARS coronavirus spike protein in virus neutralization and blocking of receptor binding: implications for the functional roles of S2 subunit
- PMID: 16989815
- PMCID: PMC7094555
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.08.085
Quantitative comparison of the efficiency of antibodies against S1 and S2 subunit of SARS coronavirus spike protein in virus neutralization and blocking of receptor binding: implications for the functional roles of S2 subunit
Abstract
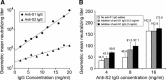
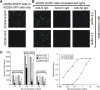
Neutralizing effects of antibodies targeting the C-terminal stalk (S2) subunit of the spike protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus have previously been reported, although its mechanism remained elusive. In this study, high titered mouse antisera against the N-terminal globular (S1) and S2 subunits of the S protein were generated and total immunoglobulin G (IgG) was purified from these antisera. The efficiency of these purified IgGs in virus neutralization and blocking of receptor binding were compared quantitatively using virus neutralization assay and a previously developed cell-based receptor binding assay, respectively. We demonstrated that anti-S1 IgG neutralizes the virus and binds to the membrane associated S protein more efficiently than anti-S2 IgG does. Moreover, both anti-S1 and anti-S2 IgGs were able to abolish the binding between S protein and its cellular receptor(s), although anti-S1 IgG showed a significantly higher blocking efficiency. The unexpected blocking ability of anti-S2 IgG towards the receptor binding implied a possible role of the S2 subunit in virus docking process and argues against the current hypothesis of viral entry. On the other hand, the functional roles of the previously reported neutralizing epitopes within S2 subunit were investigated using an antigen specific antibody depletion assay. Depletion of antibodies against these regions significantly diminished, though not completely abolished, the neutralizing effects of anti-S2 IgG. It suggests the absence of a major neutralizing domain on S2 protein. The possible ways of anti-S2 IgGs to abolish the receptor binding and the factors restricting anti-S2 IgGs to neutralize the virus are discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts declared.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

