Vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA and protein do not change in parallel during non-inflammatory skeletal muscle ischaemia in rat
- PMID: 16990404
- PMCID: PMC1890445
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.113357
Vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA and protein do not change in parallel during non-inflammatory skeletal muscle ischaemia in rat
Abstract
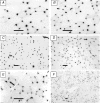
Impaired blood flow is thought to induce a pro-angiogenic environment due to local hypoxia, yet prolonged mild ischaemia induces only modest capillary growth. We compared the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA and protein with capillary to fibre ratio (C: F) and muscle blood flow in extensor digitorum longus of rats that had undergone unilateral ligation of the common iliac artery. Resting blood flow during the first two weeks after ligation (3, 7 and 14 days) was decreased by approximately 60% but recovered partially after 5 weeks (36% reduction). Functional hyperaemia (9-fold increase in blood flow during contractions) was eliminated in the first week after ligation, with a moderate recovery seen after 14 and 35 days. Muscle histology confirmed the absence of tissue necrosis or inflammation. Both VEGF mRNA (60%, P<0.05) and protein levels (700%, P<0.01) increased during the initial phase of ischaemia (at 1 and 3 days), well before any overt angiogenesis, and both declined towards control levels by 7 days. A secondary increase in VEGF protein (by 60% at 14 days, P<0.05) preceded the 20% increase in C: F seen after 5 weeks, but occurred while VEGF transcript levels continued to decline (to 50% of control at 35 days, P<0.05). Thus, evaluation of neither VEGF mRNA nor protein is an adequate index of angiogenic potential in response to ischaemia. We conclude that VEGF alone is insufficient to induce angiogenesis in ischaemic conditions, and that effective angiotherapy requires intervention aimed at other cytokines.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson SI, Hudlicka O, Brown MD. Capillary red blood cell flow and activation of white blood cells in chronic muscle ischemia in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:H2757–H2764. - PubMed
-
- Askew CD, Green S, Walker PJ, Kerr GK, Green AA, Williams AD, Febbraio MA. Skeletal muscle phenotype is associated with exercise tolerance in patients with peripheral arterial disease. J Vasc Surg. 2005;41:802–807. - PubMed
-
- Baum O, Djonov V, Ganster M, Widmer M, Baumgartner I. Arteriolarization of capillaries and FGF-2 upregulation in skeletal muscles of patients with chronic peripheral arterial disease. Microcirculation. 2005;12:527–537. - PubMed
-
- Brown MD, Kent J, Kelsall CJ, Milkiewicz M, Hudlicka O. Remodeling in the microcirculation of rat skeletal muscle during chronic ischemia. Microcirculation. 2003;10:179–191. - PubMed
-
- Brown MD, Verhaeg J, Milkiewicz M, Lamont P, Stewart A. Capillarity and vascular endothelial growth factor in calf biopsies from patients with intermittent claudication after a supervised exercise programme. J Vasc Res. 2002;39(Suppl. 1):45. abstract.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

