A family of glutamate receptor genes: evidence for the formation of heteromultimeric receptors with distinct channel properties
- PMID: 1699567
- PMCID: PMC4481242
- DOI: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90212-x
A family of glutamate receptor genes: evidence for the formation of heteromultimeric receptors with distinct channel properties
Abstract
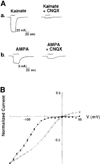
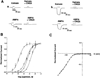
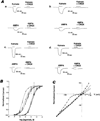
We have isolated two cDNA clones (GluR-K2 and GluR-K3) that share considerable sequence identity with the previously described glutamate receptor subunit, GluR-K1. The three glutamate receptor subunits show significant sequence conservation with the glutamine binding component of the glutamine permease of E. coli. Each of these clones encodes a channel responsive to both kainate and AMPA. The coexpression of GluR-K2 with either GluR-K3 or GluR-K1 results in the formation of channels whose current-voltage relationships differ from those of the individual subunits alone and more closely approximate the properties of kainate receptors in neurons. These observations indicate that the kainate/quisqualate receptors are encoded by a family of genes and are likely to be composed of hetero-oligomers of at least two distinct subunits.
Figures


References
-
- Ames GF-L. Bacterial periplasmic transport systems: structure, mechanism, and evolution. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1986;55:397–425. - PubMed
-
- Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
-
- Christie MI, North RA, Osborne PB, Douglass J, Adelman JP. Heteropolymeric potassium channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes from cloned subunits. Neuron. 1990;4:405–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

