Potential role of natural killer cells in controlling growth and infiltration of AIDS-associated primary effusion lymphoma cells
- PMID: 16995875
- PMCID: PMC11158791
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00319.x
Potential role of natural killer cells in controlling growth and infiltration of AIDS-associated primary effusion lymphoma cells
Abstract
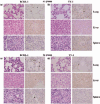
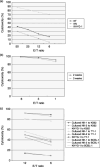
Natural killer (NK) cells are an important component of the innate immune response against microbial infections and tumors. Direct involvement of NK cells in tumor growth and infiltration has not yet been demonstrated clearly. Primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) cells were able to produce tumors and ascites very efficiently with infiltration of cells in various organs of T-, B- and NK-cell knock-out NOD/SCID/gammac(null) (NOG) mice within 3 weeks. In contrast, PEL cells formed small tumors at inoculated sites in T- and B-cell knock-out NOD/SCID mice with NK-cells while completely failing to infiltrate into various organs. Immunosupression of NOD/SCID by treatment with an antimurine TM-beta1 antibody, which transiently abrogates NK cell activity in vivo, resulted in enhanced tumorigenicity and organ infiltration in comparison with non-treated NOD/SCID mice. Activated human NK cells inhibited tumor growth and infiltration in NOG mice. Our results suggest that NK cells play an important role in growth and infiltration of PEL cells, and activated NK cells could be a promising immunotherapeutic tool against tumor or virus-infected cells either alone or in combination with conventional therapy. The rapid and efficient engraftment of PEL cells in NOG mice also suggests that this new animal model could provide a unique opportunity to understand and investigate the mechanism of pathogenesis and malignant cell growth.
Figures



References
-
- Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW, eds. World Health Organization Classification of Tumors, Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon, France: IARC Press, 2001.
-
- Gaidano G, Carbone A. Primary effusion lymphoma: a liquid phase lymphoma of fluid‐filled body cavities. Adv Cancer Res 2001; 80: 115–46. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman E, Knowles DM. The role of Kaposi's sarcoma‐associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV‐8) in lymphoproliferative diseases. Semin Cancer Biol 1999; 9: 165–74. - PubMed
-
- Klein U, Gloghini A, Gaidano G et al. Gene expression profile analysis of AIDS‐related primary effusion lymphoma (PEL) suggests a plasmablastic derivation and identifies PEL‐specific transcripts. Blood 2003; 102: 4115–21. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW, Knowles DM. Kaposi's sarcoma‐associated herpesvirus‐like DNA sequences in AIDS‐related body‐cavity‐based lymphomas. N Engl J Med 1995; 332: 1186–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

