Pattern of hemodynamic impairment in multiple sclerosis: dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion MR imaging at 3.0 T
- PMID: 16996280
- PMCID: PMC1752216
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.08.008
Pattern of hemodynamic impairment in multiple sclerosis: dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion MR imaging at 3.0 T
Abstract
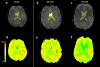
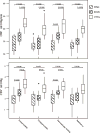
This study aimed to determine regional pattern of tissue perfusion in the normal-appearing white matter (NAWM) of patients with primary-progressive (PP), relapsing-remitting (RR) multiple sclerosis (MS) and healthy controls, and to investigate the association between perfusion abnormalities and clinical disability. Using dynamic susceptibility contrast (DSC) perfusion MRI at 3 T, we studied 22 patients with clinically definite MS, 11 with PP-MS and 11 with RR-MS and 11 age- and gender-matched healthy volunteers. The MRI protocol included axial dual-echo, dynamic susceptibility contrast enhanced (DSC) T2*-weighted and post-contrast T1-weighted images. Absolute cerebral blood flow (CBF), cerebral blood volume (CBV) and mean transit time (MTT) were measured in the periventricular, frontal, occipital NAWM and in the splenium of the corpus callosum. Compared to controls, CBF and CBV were significantly lower in all NAWM regions in both PP-MS patients (p values from <0.0001 to 0.001) and RR-MS (p values from <0.0001 to 0.020). Compared to RR-MS, PP-MS patients showed significantly lower CBF in the periventricular NAWM (p=0.002) and lower CBV in the periventricular and frontal NAWM (p values: 0.0029 and 0.022). EDSS was significantly correlated with the periventricular CBF (r=-0.48, p=0.0016) and with the periventricular and frontal CBV (r=-0.42, p=0.015; r=-0.35, p=0.038, respectively). This study suggests that the hemodynamic abnormalities of NAWM have clinical relevance in patients with MS. DSC perfusion MRI might provide a relevant objective measure of disease activity and treatment efficacy.
Figures
References
-
- Adams CW, Poston RN, Buk SJ, Sidhu YS, Vipond H. Inflammatory vasculitis in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 1985;69:269–283. - PubMed
-
- Adams RA, Passino M, Sachs BD, Nuriel T, Akassoglou K. Fibrin mechanisms and functions in nervous system pathology. Mol Interv. 2004;4:163–176. - PubMed
-
- Axel L. Cerebral blood flow determination by rapid-sequence computed tomography: theoretical analysis. Radiology. 1980;137:679–686. - PubMed
-
- Bermel RA, Sharma J, Tjoa CW, Puli SR, Bakshi R. A semiautomated measure of whole-brain atrophy in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 2003;208:57–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

