Preparation and immunogenic properties of a recombinant West Nile subunit vaccine
- PMID: 16996661
- PMCID: PMC1839850
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.08.018
Preparation and immunogenic properties of a recombinant West Nile subunit vaccine
Abstract
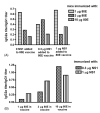
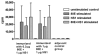
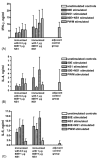
While several West Nile vaccines are being developed, none are yet available for humans. In this study aimed at developing a vaccine for humans, West Nile virus (WNV) envelope protein (E) and non-structural protein 1 (NS1) were produced in the Drosophila S2 cell expression system. The C-terminal 20% of the E protein, which contains the membrane anchor portion, was deleted, thus allowing for efficient secretion of the truncated protein (80E) into the cell culture medium. The proteins were purified by immunoaffinity chromatography (IAC) using monoclonal antibodies that were flavivirus envelope protein group specific (for the 80E) or flavivirus NS1 group specific (for NS1). The purified proteins were produced in high yield and used in conjunction with adjuvant formulations to vaccinate mice. The mice were tested for both humoral and cellular immune responses by a plaque reduction neutralization test and ELISA, and by lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine production assays, respectively. The results revealed that the 80E and the NS1 proteins induced both high-titered ELISA and neutralizing antibodies in mice. Splenocytes from immunized mice, cultured in vitro with the vaccine antigens as stimulants, showed excellent proliferation and production of cytokines (IFN-gamma, IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10). The level of antigen-stimulated lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine production was comparable to the level obtained from mitogen (phytohemagglutinin or pokeweed) stimulation, indicating a robust cellular response as well. These findings are encouraging and warrant further in vivo studies to determine the protective efficacy of the WNV vaccine candidate.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a recombinant subunit West Nile virus vaccine in rhesus monkeys.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009 Sep;16(9):1332-7. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00119-09. Epub 2009 Jul 29. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19641099 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization of flavivirus West Nile recombinant envelope domain III protein induced specific immune response and protection against West Nile virus infection.J Immunol. 2007 Mar 1;178(5):2699-705. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.5.2699. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17312111
-
Efficacy and durability of a recombinant subunit West Nile vaccine candidate in protecting hamsters from West Nile encephalitis.Vaccine. 2007 Apr 12;25(15):2913-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.08.008. Epub 2006 Aug 22. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17067727 Free PMC article.
-
The structural immunology of antibody protection against West Nile virus.Immunol Rev. 2008 Oct;225:212-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00676.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18837784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yellow fever vector live-virus vaccines: West Nile virus vaccine development.Trends Mol Med. 2001 Aug;7(8):350-4. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4914(01)02048-2. Trends Mol Med. 2001. PMID: 11516995 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vaccines in development against West Nile virus.Viruses. 2013 Sep 30;5(10):2384-409. doi: 10.3390/v5102384. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 24084235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Synthetic TLR-4 Agonist Adjuvant Increases the Protective Response to a Clinical-Stage West Nile Virus Vaccine Antigen in Multiple Formulations.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 22;11(2):e0149610. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149610. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26901122 Free PMC article.
-
The recombinant truncated envelope protein of West Nile virus adjuvanted with Alum/CpG induces potent humoral and T cell immunity in mice.Biosaf Health. 2023 Jun 27;5(5):300-307. doi: 10.1016/j.bsheal.2023.06.003. eCollection 2023 Oct. Biosaf Health. 2023. PMID: 40078908 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant Zika Virus Subunits Are Immunogenic and Efficacious in Mice.mSphere. 2018 Jan 10;3(1):e00576-17. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00576-17. eCollection 2018 Jan-Feb. mSphere. 2018. PMID: 29359186 Free PMC article.
-
A Recombinant Subunit Based Zika Virus Vaccine Is Efficacious in Non-human Primates.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 8;9:2464. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02464. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30467501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Petersen LR, Roehrig JT, Hughes JM. West Nile virus encephalitis. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1225–6. - PubMed
-
- CDC West Nile Virus website: Statistics, Surveillance, and Control. http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dvbid/westnile/surv&controlCaseCount06detailed....
-
- Komar N, Clark GG. West Nile virus activity in Latin America and the Caribbean. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2006;19:112–7. - PubMed
-
- Mostashari F, Bunning ML, Kitsutani PT, Singer DA, Nash D, Cooper MJ, et al. Epidemic West Nile encephalitis, New York, 1999, results of a household-based seroepidemiological survey. Lancet. 2001;358:261–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1 R43 AI052600-01A1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R43 AI052600-01A1/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI30027/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R44 NS052139/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 9 R44 NS52139-02A1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R44 NS052139-03/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI 25489/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R44 NS052139-04/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI030027/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R44 NS052139-02A1S1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R44 NS052139-02A1/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI025489/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

