Yeast sphingolipids: recent developments in understanding biosynthesis, regulation, and function
- PMID: 16997623
- PMCID: PMC1868558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.08.005
Yeast sphingolipids: recent developments in understanding biosynthesis, regulation, and function
Abstract
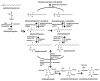
Sphingolipids function as required membrane components of virtually all eukaryotic cells. Data indicate that members of the sphingolipid family of lipids, including sphingoid bases, sphingoid base phosphates, ceramides, and complex sphingolipids, serve vital functions in cell biology by both direct mechanisms (e.g., binding to G-protein coupled receptors to transduce an extracellular signal) and indirect mechanisms (e.g., facilitating correct intracellular protein transport). Because of the diverse roles these lipids play in cell biology, it is important to understand not only their biosynthetic pathways and regulation of sphingolipid synthesis, but also the mechanisms by which some sphingolipid species with specific functions are modified or converted to other sphingolipid species with alternate functions. Due to many factors including ease of culture and genetic modification, and conservation of major sphingolipid metabolic pathways, Saccharomyces cerevisiae has served as an ideal model system with which to identify enzymes of sphingolipid biosynthesis and to dissect sphingolipid function. Recent exciting developments in sphingolipid synthesis, transport, signaling, and overall biology continue to fuel vigorous investigation and inspire investigations in mammalian sphingolipid biology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolism and selected functions of sphingolipids in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Jun 10;1438(3):305-21. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(99)00068-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. PMID: 10366774 Review.
-
Modulation of sphingolipid metabolism by the phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate phosphatase Sac1p through regulation of phosphatidylinositol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 20;284(12):7588-96. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808325200. Epub 2009 Jan 12. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19139096 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingolipid functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Jun 13;1583(1):13-25. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(02)00210-x. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12069845 Review.
-
Protection mechanisms against aberrant metabolism of sphingolipids in budding yeast.Curr Genet. 2018 Oct;64(5):1021-1028. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0826-8. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29556757 Review.
-
Brave little yeast, please guide us to thebes: sphingolipid function in S. cerevisiae.Bioessays. 1999 Dec;21(12):1004-10. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199912)22:1<1004::AID-BIES4>3.0.CO;2-Y. Bioessays. 1999. PMID: 10580985 Review.
Cited by
-
The synthetic amphipathic peptidomimetic LTX109 is a potent fungicide that disturbs plasma membrane integrity in a sphingolipid dependent manner.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 12;8(7):e69483. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069483. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23874964 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulating sphingolipid synthesis increases yeast lifespan.PLoS Genet. 2012 Feb;8(2):e1002493. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002493. Epub 2012 Feb 2. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22319457 Free PMC article.
-
Ceramides: Nutrient Signals that Drive Hepatosteatosis.J Lipid Atheroscler. 2020 Jan;9(1):50-65. doi: 10.12997/jla.2020.9.1.50. Epub 2019 Nov 13. J Lipid Atheroscler. 2020. PMID: 32821721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genome-wide enhancer screen implicates sphingolipid composition in vacuolar ATPase function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2011 Mar;187(3):771-83. doi: 10.1534/genetics.110.125567. Epub 2010 Dec 31. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 21196517 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel SPT inhibitor WXP-003 by docking-based virtual screening and investigation of its anti-fungi effect.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021 Dec;36(1):1007-1015. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2021.1915301. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34148472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El Alwani M, Wu BX, Obeid LM, Hannun YA. Bioactive sphingolipids in the modulation of the inflammatory response. Pharmacol Ther. 2006 - PubMed
-
- Lamour NF, Chalfant CE. Ceramide-1-phosphate: the “missing” link in eicosanoid biosynthesis and inflammation. Mol Interv. 2005;5:358–367. - PubMed
-
- Argraves KM, Wilkerson BA, Argraves WS, Fleming PA, Obeid LM, Drake CJ. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling promotes critical migratory events in vasculogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:50580–50590. - PubMed
-
- Summers SA. Ceramides in insulin resistance and lipotoxicity. Prog Lipid Res. 2006;45:42–72. - PubMed
-
- Summers SA, Nelson DH. A role for sphingolipids in producing the common features of type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome X, and Cushing’s syndrome. Diabetes. 2005;54:591–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases