Molecular characterization of the minimal replicon and the unidirectional theta replication of pSCM201 in extremely halophilic archaea
- PMID: 16997958
- PMCID: PMC1698213
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00988-06
Molecular characterization of the minimal replicon and the unidirectional theta replication of pSCM201 in extremely halophilic archaea
Abstract
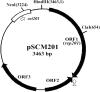
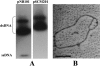
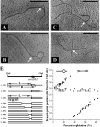
A 3,463-bp plasmid, pSCM201, was isolated from a halophilic archaeon, Haloarcula sp. strain AS7094. The minimal replicon that is essential and sufficient for autonomous replication and stable maintenance in Haloarcula hispanica was determined by deletion analysis of the plasmid. This minimal replicon ( approximately 1.8 kb) consisted of only two functionally related segments: (i) a putative origin (ori201) containing an AT-rich region and sets of repeats and (ii) an adjacent gene encoding a putative replication initiation protein (Rep201). Electron microscopic observation and Southern blotting analysis demonstrated that pSCM201 replicates via a theta mechanism. Precise mapping of the putative origin suggested that the replication initiated from a fixed site close to the AT-rich region and proceeded unidirectionally toward the downstream rep201 gene, which was further confirmed by electron microscopic analysis of the ClaI-digested replication intermediates. To our knowledge, this is the first unidirectional theta replication plasmid experimentally identified in the domain of archaea. It provides a novel plasmid system to conduct research on archaeal DNA replication.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genetic analysis of a novel plasmid pZMX101 from Halorubrum saccharovorum: determination of the minimal replicon and comparison with the related haloarchaeal plasmid pSCM201.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 May;270(1):104-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2007.00656.x. Epub 2007 Mar 16. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17371299
-
[Construction and application of a novel shuttle expression vector based on haloarchaeal plasmid pSCM201].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2009 Aug;49(8):1040-7. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2009. PMID: 19835165 Chinese.
-
An archaeal chromosomal autonomously replicating sequence element from an extreme halophile, Halobacterium sp. strain NRC-1.J Bacteriol. 2003 Oct;185(20):5959-66. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.20.5959-5966.2003. J Bacteriol. 2003. PMID: 14526006 Free PMC article.
-
Where does DNA replication start in archaea?Genome Biol. 2000;1(3):REVIEWS1020. doi: 10.1186/gb-2000-1-3-reviews1020. Genome Biol. 2000. PMID: 11521661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[DNA replication mechanism in Archaeal cells].Seikagaku. 2000 Oct;72(10):1253-8. Seikagaku. 2000. PMID: 11215147 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The global distribution and evolutionary history of the pT26-2 archaeal plasmid family.Environ Microbiol. 2019 Dec;21(12):4685-4705. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14800. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31503394 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and evolution of multiple orc/cdc6-adjacent replication origins in haloarchaea.BMC Genomics. 2012 Sep 14;13:478. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-478. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22978470 Free PMC article.
-
Choosing a suitable method for the identification of replication origins in microbial genomes.Front Microbiol. 2015 Sep 30;6:1049. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01049. eCollection 2015. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26483774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism for the TtDnaA-Tt-oriC cooperative interaction at high temperature and duplex opening at an unusual AT-rich region in Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(9):3087-99. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm137. Epub 2007 Apr 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17452366 Free PMC article.
-
One-way PCR-based mapping of a replication initiation point (RIP).Nat Protoc. 2008;3(11):1729-35. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2008.173. Nat Protoc. 2008. PMID: 18927558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allers, T., and M. Mevarech. 2005. Archaeal genetics—the third way. Nat. Rev. Genet. 6:58-73. - PubMed
-
- Baliga, N. S., R. Bonneau, M. T. Facciotti, M. Pan, G. Glusman, E. W. Deutsch, P. Shannon, Y. Chiu, R. S. Weng, R. R. Gan, P. Hung, S. V. Date, E. Marcotte, L. Hood, and W. V. Ng. 2004. Genome sequence of Haloarcula marismortui: a halophilic archaeon from the Dead Sea. Genome Res. 14:2221-2234. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernander, R. 2000. Chromosome replication, nucleoid segregation and cell division in archaea. Trends Microbiol. 8:278-283. - PubMed
-
- Bielinsky, A. K., and S. A. Gerbi. 1998. Discrete start sites for DNA synthesis in the yeast ARS1 origin. Science 279:95-98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

