Role of quorum sensing and antimicrobial component production by Serratia plymuthica in formation of biofilms, including mixed biofilms with Escherichia coli
- PMID: 16997989
- PMCID: PMC1636202
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01708-06
Role of quorum sensing and antimicrobial component production by Serratia plymuthica in formation of biofilms, including mixed biofilms with Escherichia coli
Abstract
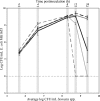
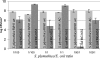
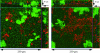
We have previously characterized the N-acyl-l-homoserine lactone-based quorum-sensing system of the biofilm isolate Serratia plymuthica RVH1. Here we investigated the role of quorum sensing and of quorum-sensing-dependent production of an antimicrobial compound (AC) on biofilm formation by RVH1 and on the cocultivation of RVH1 and Escherichia coli in planktonic cultures or in biofilms. Biofilm formation of S. plymuthica was not affected by the knockout of splI or splR, the S. plymuthica homologs of the luxI or luxR quorum-sensing gene, respectively, or by the knockout of AC production. E. coli grew well in mixed broth culture with RVH1 until the latter reached 8.5 to 9.5 log CFU/ml, after which the E. coli colony counts steeply declined. In comparison, only a very small decline occurred in cocultures with the S. plymuthica AC-deficient and splI mutants. Complementation with exogenous N-hexanoyl-l-homoserine lactone rescued the wild-type phenotype of the splI mutant. The splR knockout mutant also induced a steep decline of E. coli, consistent with its proposed function as a repressor of quorum-sensing-regulated genes. The numbers of E. coli in 3-day-old mixed biofilms followed a similar pattern, being higher with S. plymuthica deficient in SplI or AC production than with wild-type S. plymuthica, the splR mutant, or the splI mutant in the presence of N-hexanoyl-l-homoserine lactone. Confocal laser scanning microscopic analysis of mixed biofilms established with strains producing different fluorescent proteins showed that E. coli microcolonies were less developed in the presence of RVH1 than in the presence of the AC-deficient mutant.
Figures

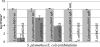
References
-
- Al-Bakri, A. G., P. Gilbert, and D. G. Allison. 2004. Immigration and emigration of Burkholderia cepacia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa between and within mixed biofilm communities. J. Appl. Microbiol. 96:455-463. - PubMed
-
- Alexeyev, M. F., and I. N. Shokolenko. 1995. Mini-Tn10 transposon derivatives for insertion mutagenesis and gene delivery into the chromosome of gram-negative bacteria. Gene 160:59-62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

