The Arabidopsis tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein TTL1 is required for osmotic stress responses and abscisic acid sensitivity
- PMID: 16998088
- PMCID: PMC1630727
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.085191
The Arabidopsis tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein TTL1 is required for osmotic stress responses and abscisic acid sensitivity
Abstract
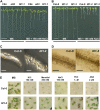
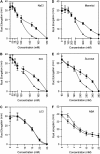
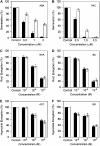
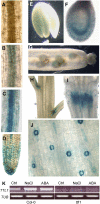
Mutations in the Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) TETRATRICOPEPTIDE-REPEAT THIOREDOXIN-LIKE 1 (TTL1) cause reduced tolerance to NaCl and osmotic stress that is characterized by reduced root elongation, disorganization of the root meristem, and impaired osmotic responses during germination and seedling development. Expression analyses of genes involved in abscisic acid (ABA) biosynthesis and catabolism suggest that TTL1 is not involved in the regulation of ABA levels but is required for ABA-regulated responses. TTL1 regulates the transcript levels of several dehydration-responsive genes, such as the transcription factor DREB2A, and genes encoding dehydration response proteins, such as ERD1 (early response to dehydration 1), ERD3, and COR15a. The TTL1 gene encodes a novel plant protein with tetratricopeptide repeats and a region with homology to thioredoxin proteins. Based on homology searches, there are four TTL members in the Arabidopsis genome with similar intron-exon structure and conserved amino acid domains. Proteins containing tetratricopeptide repeat motifs act as scaffold-forming multiprotein complexes and are emerging as essential elements for plant hormonal responses (such as gibberellin responses and ethylene biosynthesis). In this report, we identify TTL1 as a positive regulator of ABA signaling during germination and seedling development under stress.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Arabidopsis thaliana ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE8 encodes a novel protein mediating abscisic acid and sugar responses essential for growth.Plant Cell. 2004 Feb;16(2):406-21. doi: 10.1105/tpc.018077. Epub 2004 Jan 23. Plant Cell. 2004. PMID: 14742875 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis tetratricopeptide thioredoxin-like gene family is required for osmotic stress tolerance and male sporogenesis.Plant Physiol. 2012 Mar;158(3):1252-66. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.188920. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22232384 Free PMC article.
-
An ABRE promoter sequence is involved in osmotic stress-responsive expression of the DREB2A gene, which encodes a transcription factor regulating drought-inducible genes in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell Physiol. 2011 Dec;52(12):2136-46. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcr143. Epub 2011 Oct 24. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 22025559
-
Knockout of AtDjB1, a J-domain protein from Arabidopsis thaliana, alters plant responses to osmotic stress and abscisic acid.Physiol Plant. 2014 Oct;152(2):286-300. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12169. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Physiol Plant. 2014. PMID: 24521401
-
The ethylene response factor AtERF11 that is transcriptionally modulated by the bZIP transcription factor HY5 is a crucial repressor for ethylene biosynthesis in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2011 Oct;68(1):88-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04670.x. Epub 2011 Jul 21. Plant J. 2011. PMID: 21645149
Cited by
-
Global Scale Transcriptional Profiling of Two Contrasting Barley Genotypes Exposed to Moderate Drought Conditions: Contribution of Leaves and Crowns to Water Shortage Coping Strategies.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Dec 27;7:1958. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01958. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 28083001 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating Arabidopsis Primary Root Growth in Response to Osmotic Stress Using an In Vitro Osmotic Gradient Experimental System.Bio Protoc. 2025 Jul 20;15(14):e5397. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.5397. eCollection 2025 Jul 20. Bio Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40741399 Free PMC article.
-
De novo transcriptome assembly and analysis of differentially expressed genes of two barley genotypes reveal root-zone-specific responses to salt exposure.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 16;6:31558. doi: 10.1038/srep31558. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27527578 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals crosstalk of responsive genes to multiple abiotic stresses in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.).PLoS One. 2013 Nov 5;8(11):e80218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080218. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24224045 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis TETRATRICOPEPTIDE THIOREDOXIN-LIKE 1 Gene Is Involved in Anisotropic Root Growth during Osmotic Stress Adaptation.Genes (Basel). 2021 Feb 7;12(2):236. doi: 10.3390/genes12020236. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33562207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blatch GL, Lässle M (1999) The tetratricopeptide repeat: a structural motif mediating protein-protein interactions. Bioessays 21: 932–939 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

