Distinct and gradient distributions of connexin26 and connexin30 in the cochlear sensory epithelium of guinea pigs
- PMID: 16998915
- PMCID: PMC2553046
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.21113
Distinct and gradient distributions of connexin26 and connexin30 in the cochlear sensory epithelium of guinea pigs
Abstract
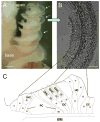
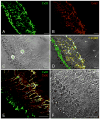
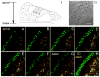
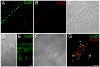
Connexin26 (Cx26) and Cx30 are predominant isoforms of gap junction channels in the cochlea and play a critical role in hearing. In this study, the cellular distributions of Cx26 and Cx30 in the cochlear sensory epithelium of guinea pigs were examined by immunofluorescent staining and confocal microscopy in whole mounts of the cochlear sensory epithelium and dissociated cell preparations. The expression of Cx26 and Cx30 demonstrated a longitudinal gradient distribution in the epithelium and was reduced threefold from the cochlear apex to base. The reduction was more pronounced in the Deiters cells and pillar cells than in the Hensen cells. Cx26 was expressed in all types of supporting cells, but little Cx30 labeling was seen in the Hensen cells. Cx26 expression in the Hensen cells was concentrated mainly in the second and third rows, forming a distinct band along the sensory epithelium at its outer region. In the dissociated Deiters cells and pillar cells, Cx30 showed dense labeling at the cell bodies and processes in the reticular lamina. Cx26 labeling largely overlapped that of Cx30 in these regions. Cx26 and Cx30 were also coexpressed in the gap junctional plaques between Claudius cells. Neither Cx26 nor Cx30 labeling was seen in the hair cells and spiral ganglion neurons. These observations demonstrate that Cx26 and Cx30 have a longitudinal gradient distribution and distinct cellular expression in the auditory sensory epithelium. This further supports our previous reports that Cx26 and Cx30 can solely and concertedly perform different functions in the cochlea.
Figures






References
-
- Beltramello M, Bicego M, Piazza V, Ciubotaru CD, Mammano F, D’Andrea P. Permeability and gating properties of human connexins 26 and 30 expressed in HeLa cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;305:1024–1033. - PubMed
-
- Bruzzone R, Veronesi V, Gomes D, Bicego M, Duval N, Marlin S, Petit C, D’Andrea P, White TW. Loss-of-function and residual channel activity of connexin26 mutations associated with nonsyndromic deafness. FEBS Lett. 2003;533:79–88. - PubMed
-
- Choung YH, Moon SK, Park HJ. Functional study of GJB2 in hereditary hearing loss. Laryngoscope. 2002;112:1667–1671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

