Normal establishment of epithelial tight junctions in mice and cultured cells lacking expression of ZO-3, a tight-junction MAGUK protein
- PMID: 17000770
- PMCID: PMC1636814
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01811-05
Normal establishment of epithelial tight junctions in mice and cultured cells lacking expression of ZO-3, a tight-junction MAGUK protein
Abstract
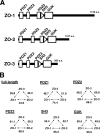
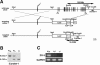
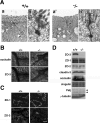
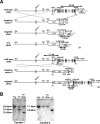
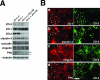
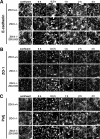
ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3 are closely related MAGUK family proteins that localize at the cytoplasmic surface of tight junctions (TJs). ZO-1 and ZO-2 are expressed in both epithelia and endothelia, whereas ZO-3 is exclusively expressed in epithelia. In spite of intensive studies of these TJ MAGUKs, our knowledge of their functions in vivo, especially those of ZO-3, is still fragmentary. Here, we have generated mice, as well as F9 teratocarcinoma cell lines, that do not express ZO-3 by homologous recombination. Unexpectedly, ZO-3(-/-) mice were viable and fertile, and rigorous phenotypic analyses identified no significant abnormalities. Moreover, ZO-3-deficient F9 teratocarcinoma cells differentiated normally into visceral endoderm epithelium-like cells in the presence of retinoic acid. These cells had a normal epithelial appearance, and the molecular architecture of their TJs did not appear to be affected, except that TJ localization of ZO-2 was upregulated. Suppression of ZO-2 expression by RNA interference in ZO-3(-/-) cells, however, did not affect the architecture of TJs. Furthermore, the speed with which TJs formed after a Ca(2+) switch was indistinguishable between wild-type and ZO-3(-/-) cells. These findings indicate that ZO-3 is dispensable in vivo in terms of individual viability, epithelial differentiation, and the establishment of TJs, at least in the laboratory environment.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson, J. M., and C. M. Van Itallie. 1995. Tight junctions and the molecular basis for regulation of paracellular permeability. Am. J. Physiol. 269:G467-G475. - PubMed
-
- Ando-Akatsuka, Y., S. Yonemura, M. Itoh, M. Furuse, and S. Tsukita. 1999. Differential behavior of E-cadherin and occludin in their colocalization with ZO-1 during the establishment of epithelial cell polarity. J. Cell Physiol. 179:115-125. - PubMed
-
- Balda, M. S., and K. Matter. 1998. Tight junctions. J. Cell Sci. 111:541-547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
