Mechanism of transport of IFT particles in C. elegans cilia by the concerted action of kinesin-II and OSM-3 motors
- PMID: 17000880
- PMCID: PMC2064394
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200606003
Mechanism of transport of IFT particles in C. elegans cilia by the concerted action of kinesin-II and OSM-3 motors
Abstract
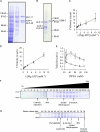
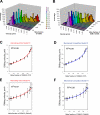
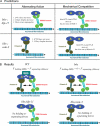
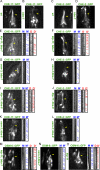
The assembly and function of cilia on Caenorhabditis elegans neurons depends on the action of two kinesin-2 motors, heterotrimeric kinesin-II and homodimeric OSM-3-kinesin, which cooperate to move the same intraflagellar transport (IFT) particles along microtubule (MT) doublets. Using competitive in vitro MT gliding assays, we show that purified kinesin-II and OSM-3 cooperate to generate movement similar to that seen along the cilium in the absence of any additional regulatory factors. Quantitative modeling suggests that this could reflect an alternating action mechanism, in which the motors take turns to move along MTs, or a mechanical competition, in which the motors function in a concerted fashion to move along MTs with the slow motor exerting drag on the fast motor and vice versa. In vivo transport assays performed in Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS) protein and IFT motor mutants favor a mechanical competition model for motor coordination in which the IFT motors exert a BBS protein-dependent tension on IFT particles, which controls the IFT pathway that builds the cilium foundation.
Figures
References
-
- Ansley, S.J., J.L. Badano, O.E. Blacque, J. Hill, B.E. Hoskins, C.C. Leitch, J.C. Kim, A.J. Ross, E.R. Eichers, T.M. Teslovich, et al. 2003. Basal body dysfunction is a likely cause of pleiotropic Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Nature. 425:628–633. - PubMed
-
- Badano, J.L., N. Mitsuma, P.L. Beales, and N. Katsanis. 2006. The ciliopathies: an emerging class of human genetic disorders. Annu. Rev. Genomics. Hum. Genet. 7:125–148. - PubMed
-
- Beales, P.L. 2005. Lifting the lid on Pandora's box: the Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 15:315–323. - PubMed
-
- Berezuk, M.A., and T.A. Schroer. 2004. Fractionation and characterization of kinesin II species in vertebrate brain. Traffic. 5:503–513. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

