Functional analysis of members of the isoflavone and isoflavanone O-methyltransferase enzyme families from the model legume Medicago truncatula
- PMID: 17001495
- PMCID: PMC2862459
- DOI: 10.1007/s11103-006-9050-x
Functional analysis of members of the isoflavone and isoflavanone O-methyltransferase enzyme families from the model legume Medicago truncatula
Abstract
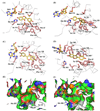
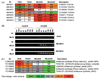
Previous studies have identified two distinct O-methyltransferases (OMTs) implicated in isoflavonoid biosynthesis in Medicago species, a 7-OMT methylating the A-ring 7-hydroxyl of the isoflavone daidzein and a 4'-OMT methylating the B-ring 4'-hydroxyl of 2,7,4'-trihydroxyisoflavanone. Genes related to these OMTs from the model legume Medicago truncatula cluster as separate branches of the type I plant small molecule OMT family. To better understand the possible functions of these related OMTs in secondary metabolism in M. truncatula, seven of the OMTs were expressed in E. coli, purified, and their in vitro substrate preferences determined. Many of the enzymes display promiscuous activities, and some exhibit dual regio-specificity for the 4' and 7-hydroxyl moieties of the isoflavonoid nucleus. Protein structure homology modeling was used to help rationalize these catalytic activities. Transcripts encoding the different OMT genes exhibited differential tissue-specific and infection- or elicitor-induced expression, but not always in parallel with changes in expression of confirmed genes of the isoflavonoid pathway. The results are discussed in relation to the potential in vivo functions of these OMTs based on our current understanding of the phytochemistry of M. truncatula, and the difficulties associated with gene annotation in plant secondary metabolism.
Figures






References
-
- Akashi T, Sawada Y, Aoki T, Ayabe S-I. New scheme of the biosynthesis of formononetin involving 2,7,4′-trihydroxyisoflavanone but not daidzein as the methyl acceptor. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2000;64:2276–2279. - PubMed
-
- Akashi T, Sawada Y, Shimada H, Sakurai N, Aoki T, Ayabe S. cDNA cloning and biochemical characterization of S-adenosyl-L-methionine: 2,7,4′-trihydroxyisoflavanone 4′-O-methyltransferase, a critical enzyme of the legume isoflavonoid phytoalexin pathway. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003;44:103–112. - PubMed
-
- Bisby FA, Buckingham J, Harborne JB, editors. Plants and their constituents. New York: Chapman and Hall; 1994. Phytochemical dictionary of the Leguminosae, Vol I.
-
- Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

