Tropomodulin binds two tropomyosins: a novel model for actin filament capping
- PMID: 17002306
- PMCID: PMC2596622
- DOI: 10.1021/bi060899i
Tropomodulin binds two tropomyosins: a novel model for actin filament capping
Abstract
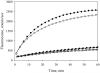
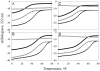
Tropomodulin, a tropomyosin-binding protein, caps the slow-growing (pointed) end of the actin filament regulating its dynamics. Tropomodulin, therefore, is important for determining cell morphology, cell movement, and muscle contraction. For the first time we show that one tropomodulin molecule simultaneously binds two tropomyosin molecules in a cooperative manner. On the basis of the tropomodulin solution structure and predicted secondary structure, we introduced a series of point mutations in regions important for tropomyosin binding and actin capping. Capping activity of these mutants was assayed by measuring actin polymerization using pyrene fluorescence. Using direct methods (circular dichroism and native gel electrophoresis) for detecting tropomodulin/tropomyosin binding, we localized the second tropomyosin-binding site to residues 109-144. Despite previous reports that the second binding site is for erythrocyte tropomyosin only, we found that both short nonmuscle and long muscle alpha-tropomyosins bind there as well, though with different affinities. We propose a model for actin capping where one tropomodulin molecule can bind to two tropomyosin molecules at the pointed end.
Figures






References
-
- Pollard TD, Borisy GG. Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell. 2003;112:453–65. - PubMed
-
- Rafelski SM, Theriot JA. Crawling toward a unified model of cell mobility: spatial and temporal regulation of actin dynamics. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:209–39. - PubMed
-
- Carlier MF, Pantaloni D. Control of actin dynamics in cell motility. J Mol Biol. 1997;269:459–67. - PubMed
-
- dos Remedios CG, Chhabra D, Kekic M, Dedova IV, Tsubakihara M, Berry DA, Nosworthy NJ. Actin binding proteins: regulation of cytoskeletal microfilaments. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:433–73. - PubMed
-
- Perry SV. Vertebrate tropomyosin: distribution, properties and function. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2001;22:5–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

