Inhalation of the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 reverses allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness after the early and late asthmatic reaction
- PMID: 17002806
- PMCID: PMC1586199
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-121
Inhalation of the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 reverses allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness after the early and late asthmatic reaction
Abstract
Background: In guinea pigs, we have previously demonstrated that the contribution of Rho-kinase to airway responsiveness in vivo and ex vivo is enhanced after active sensitization with ovalbumin (OA). Using conscious, unrestrained OA-sensitized guina pigs, we now investigated the role of Rho-kinase in the development of airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) after the allergen-induced early (EAR) and late asthmatic reaction (LAR) in vivo.
Methods: Histamine and PGF2alpha PC100-values (provocation concentrations causing 100% increase in pleural pressure) were assessed before OA-challenge (basal airway responsiveness) and after the OA-induced EAR (5 h after challenge) and LAR (23 h after challenge). Thirty minutes later, saline or the specific Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (5 mM, nebulizer concentration) were nebulized, after which PC100-values were reassessed.
Results: In contrast to saline, Y-27632 inhalation significantly decreased the basal responsiveness toward histamine and PGF2alpha before OA-challenge, as indicated by increased PC100 -values. Both after the allergen-induced EAR and LAR, AHR to histamine and PGF2alpha was present, which was reversed by Y-27632 inhalation. Moreover, there was an increased effectiveness of Y-27632 to reduce airway responsiveness to histamine and PGF2alpha after the EAR and LAR as compared to pre-challenge conditions. Saline inhalations did not affect histamine or PGF2alpha PC100-values at all. Interestingly, under all conditions Y-27632 was significantly more effective in reducing airway responsiveness to PGF2alpha as compared to histamine. Also, there was a clear tendency (P = 0.08) to a more pronounced degree of AHR after the EAR for PGF2alpha than for histamine.
Conclusion: The results indicate that inhalation of the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 causes a considerable bronchoprotection to both histamine and PGF2alpha. Moreover, the results are indicative of a differential involvement of Rho-kinase in the agonist-induced airway obstruction in vivo. Increased Rho-kinase activity contributes to the allergen-induced AHR to histamine and PGF2alpha after both the EAR and the LAR, which is effectively reversed by inhalation of Y-27632. Therefore, Rho-kinase can be considered as a potential pharmacotherapeutical target in allergic asthma.
Figures
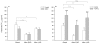
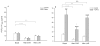

Similar articles
-
Allergic sensitization enhances the contribution of Rho-kinase to airway smooth muscle contraction.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Oct;143(4):477-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705903. Epub 2004 Sep 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15381630 Free PMC article.
-
The inhaled Rho kinase inhibitor Y-27632 protects against allergen-induced acute bronchoconstriction, airway hyperresponsiveness, and inflammation.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 Jul;295(1):L214-9. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00498.2007. Epub 2008 May 16. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18487358
-
Inhibition of Rho-kinase normalizes nonspecific hyperresponsiveness in passively sensitized airway smooth muscle preparations.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Feb 15;531(1-3):145-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.043. Epub 2006 Jan 31. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16451800
-
[Allergic inflammation in the development of nonspecific bronchial hyperresponsiveness in asthma].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2002 Jun;12(72):515-8. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2002. PMID: 12362673 Review. Polish.
-
On the role of PGD2 metabolites as markers of mast cell activation in asthma.Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1999 Apr;644:1-74. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1999. PMID: 10352758 Review.
Cited by
-
Abrogation of airway hyperresponsiveness but not inflammation by rho kinase insufficiency.Clin Exp Allergy. 2015 Feb;45(2):457-70. doi: 10.1111/cea.12438. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015. PMID: 25323425 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor-β enhances Rho-kinase activity and contraction in airway smooth muscle via the nucleotide exchange factor ARHGEF1.J Physiol. 2018 Jan 1;596(1):47-66. doi: 10.1113/JP275033. Epub 2017 Nov 23. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29071730 Free PMC article.
-
High molecular weight hyaluronan ameliorates allergic inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in the mouse.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):L787-L798. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00009.2018. Epub 2018 Sep 6. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30188746 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Rho-kinase improves response to deep inspiration in ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Dec;23(12):1584-1589. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.46258.10683. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33489033 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Rho kinase isoforms in murine allergic airway responses.Eur Respir J. 2011 Oct;38(4):841-50. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00125010. Epub 2011 May 12. Eur Respir J. 2011. PMID: 21565918 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kharitonov SA, Sapienza MA, Barnes PJ, Chung KF. Prostaglandins E2 and F2alpha reduce exhaled nitric oxide in normal and asthmatic subjects irrespective of airway caliber changes. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;158:1374–1378. - PubMed
-
- Pfitzer G. Invited review: regulation of myosin phosphorylation in smooth muscle. J Appl Physiol. 2001;91:497–503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

