Energetics of ligand-induced conformational flexibility in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli
- PMID: 17003033
- PMCID: PMC2793331
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M607232200
Energetics of ligand-induced conformational flexibility in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli
Abstract
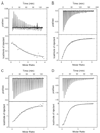
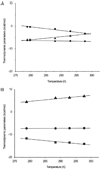
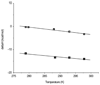
Isothermal titration calorimetry has been applied to characterize the thermodynamics of ligand binding to wild-type lactose permease (LacY) and a mutant (C154G) that strongly favors an inward facing conformation. The affinity of wild-type or mutant LacY for ligand and the change in free energy (DeltaG) upon binding are similar. However, with the wild type, the change in free energy upon binding is due primarily to an increase in the entropic free energy component (TDeltaS), whereas in marked contrast, an increase in enthalpy (DeltaH) is responsible for DeltaG in the mutant. Thus, wild-type LacY behaves as if there are multiple ligand-bound conformational states, whereas the mutant is severely restricted. The findings also indicate that the structure of the mutant represents a conformational intermediate in the overall transport cycle.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interhelical packing modulates conformational flexibility in the lactose permease of Escherichia coli.Biochemistry. 2005 May 31;44(21):7669-77. doi: 10.1021/bi0502801. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15909981
-
Structural determination of wild-type lactose permease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Sep 25;104(39):15294-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707688104. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17881559 Free PMC article.
-
[Structure and function of lactose permease from Escherichia coli].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2004 Jun;49(8):1212-8. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2004. PMID: 15209217 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Coarse-grained simulations of proton-dependent conformational changes in lactose permease.Proteins. 2016 Aug;84(8):1067-74. doi: 10.1002/prot.25053. Epub 2016 May 3. Proteins. 2016. PMID: 27090495
-
The alternating access transport mechanism in LacY.J Membr Biol. 2011 Jan;239(1-2):85-93. doi: 10.1007/s00232-010-9327-5. Epub 2010 Dec 16. J Membr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21161516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the inhibitory mechanisms of the regulatory protein IIA(Glc) on melibiose permease activity.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 21;289(47):33012-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.609255. Epub 2014 Oct 8. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25296751 Free PMC article.
-
Helix dynamics in LacY: helices II and IV.J Mol Biol. 2010 Feb 26;396(3):617-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.12.044. Epub 2010 Jan 4. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20043916 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the irreplaceable residues in the LacY alternating access mechanism.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 31;109(31):12438-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1210684109. Epub 2012 Jul 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22802658 Free PMC article.
-
Residues gating the periplasmic pathway of LacY.J Mol Biol. 2009 Nov 27;394(2):219-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.09.043. Epub 2009 Sep 23. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19781551 Free PMC article.
-
Clogging the periplasmic pathway in LacY.Biochemistry. 2009 Feb 3;48(4):738-43. doi: 10.1021/bi801976r. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19128028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaback HR. C. R. Biol. 2005;328:557–567. - PubMed
-
- Menick DR, Sarkar HK, Poonian MS, Kaback HR. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1985;132:162–170. - PubMed
-
- van Iwaarden PR, Driessen AJ, Lolkema JS, Kaback HR, Konings WN. Biochemistry. 1993;32:5419–5424. - PubMed
-
- Smirnova IN, Kaback HR. Biochemistry. 2003;42:3025–3031. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

