Evolution of variants of yeast site-specific recombinase Flp that utilize native genomic sequences as recombination target sites
- PMID: 17003057
- PMCID: PMC1635253
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkl548
Evolution of variants of yeast site-specific recombinase Flp that utilize native genomic sequences as recombination target sites
Abstract
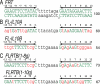
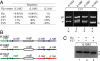
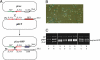
As a tool in directed genome manipulations, site-specific recombination is a double-edged sword. Exquisite specificity, while highly desirable, makes it imperative that the target site be first inserted at the desired genomic locale before it can be manipulated. We describe a combination of computational and experimental strategies, based on the tyrosine recombinase Flp and its target site FRT, to overcome this impediment. We document the systematic evolution of Flp variants that can utilize, in a bacterial assay, two sites from the human interleukin 10 gene, IL10, as recombination substrates. Recombination competence on an end target site is acquired via chimeric sites containing mixed sequences from FRT and the genomic locus. This is the first time that a tyrosine site-specific recombinase has been coaxed successfully to perform DNA exchange within naturally occurring sequences derived from a foreign genomic context. We demonstrate the ability of an Flp variant to mediate integration of a reporter cassette in Escherichia coli via recombination at one of the IL10-derived sites.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Target-specific variants of Flp recombinase mediate genome engineering reactions in mammalian cells.FEBS J. 2015 Sep;282(17):3323-33. doi: 10.1111/febs.13345. Epub 2015 Jul 1. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 26077105 Free PMC article.
-
Recombination of hybrid target sites by binary combinations of Flp variants: mutations that foster interprotomer collaboration and enlarge substrate tolerance.J Mol Biol. 2004 May 28;339(2):365-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.03.060. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15136039
-
A dual reporter screening system identifies the amino acid at position 82 in Flp site-specific recombinase as a determinant for target specificity.Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Apr 1;30(7):1656-63. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.7.1656. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. PMID: 11917027 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding Flp-RMCE options: the potential of Recombinase Mediated Twin-Site Targeting (RMTT).Gene. 2014 Aug 10;546(2):135-44. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24905650 Review.
-
New insight into site-specific recombination from Flp recombinase-DNA structures.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003;32:135-59. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.141732. Epub 2003 Feb 11. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003. PMID: 12598365 Review.
Cited by
-
Vika/vox, a novel efficient and specific Cre/loxP-like site-specific recombination system.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jan;41(2):e37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1037. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23143104 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the DNA editing toolbox: Novel lambda integrase variants targeting microalgal and human genome sequences.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 13;19(2):e0292479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292479. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38349923 Free PMC article.
-
Large T antigen mediated target gene replication improves site-specific recombination efficiency.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Apr 26;12:1377167. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1377167. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38737535 Free PMC article.
-
The partitioning and copy number control systems of the selfish yeast plasmid: an optimized molecular design for stable persistence in host cells.Microbiol Spectr. 2014 Oct;2(5):10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0003-2013. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.PLAS-0003-2013. Microbiol Spectr. 2014. PMID: 25541598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site promiscuity of coliphage HK022 integrase as a tool for gene therapy.Gene Ther. 2015 Jul;22(7):521-7. doi: 10.1038/gt.2015.9. Epub 2015 Mar 12. Gene Ther. 2015. PMID: 25762284
References
-
- Azaro M.A., Landy A. λ Integrase and λ Int family. In: Craig N.L., Craigie R., Gellert M., Lambowitz A.M., editors. Mobile DNA II. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2002. pp. 118–148.
-
- Barre F.-X., Sherratt D.J. Xer site-specific recombination: promoting chromosome segregation. In: Craig N.L., Craigie R., Gellert M., Lambowitz A.M., editors. Mobile DNA II. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2002. pp. 1149–161.
-
- Jayaram M., Grainge I., Tribble G. Site-specific recombination by the Flp protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In: Craig N.L., Craigie R., Gellert M., Lambowitz A.M., editors. Mobile DNA II. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2002. pp. 192–218.
-
- Rice P.A. Theme and variation in tyrosine recombinases: structure of a Flp-DNA complex. In: Craig N.L., Craigie R., Gellert M., Lambowitz A.M., editors. Mobile DNA II. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2002. pp. 219–229.
-
- Van Duyne G.D. A structural view of tyrosine recombinase site-specific recombination. In: Craig N.L., Craigie R., Gellert M., Lambowitz A.M., editors. Mobile DNA II. Washington, DC: ASM Press; 2002. pp. 93–117.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

