Results of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute ALL Consortium Protocol 95-01 for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- PMID: 17003366
- PMCID: PMC1785142
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-06-027714
Results of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute ALL Consortium Protocol 95-01 for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Abstract
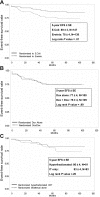
The Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI) Childhood ALL Consortium Protocol 95-01 was designed to minimize therapy-related morbidity for children with newly diagnosed ALL without compromising efficacy. Patients participated in randomized comparisons of (1) doxorubicin given with or without dexrazoxane, a cardioprotectant (high-risk patients), (2) intensive intrathecal chemotherapy and cranial radiation (standard-risk patients), and (3) Erwinia and Escherichia coli asparaginase (all patients). Between 1996 and 2000, 491 patients (aged 0-18 years) were enrolled (272 standard risk and 219 high risk). With a median of 5.7 years of follow-up, the estimated 5-year event-free survival (EFS) for all patients was 82%+/-2%. Dexrazoxane did not have a significant impact on the 5-year EFS of high-risk patients (P=.99), and there was no significant difference in outcome of standard-risk patients based on type of central nervous system (CNS) treatment (P=.26). Compared with E coli asparaginase, Erwinia asparaginase was associated with a lower incidence of toxicity (10% versus 24%), but also an inferior 5-year EFS (78%+/-4% versus 89%+/-3%, P=.01). We conclude that (1) dexrazoxane does not interfere with the antileukemic effect of doxorubicin, (2) intensive intrathecal chemotherapy is as effective as cranial radiation in preventing CNS relapse in standard-risk patients, and (3) once-weekly Erwinia is less toxic than E coli asparaginase, but also less efficacious.
Figures
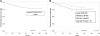
References
-
- Silverman LB, Gelber RD, Dalton VK, et al. Improved outcome for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of Dana-Farber Consortium Protocol 91-01. Blood. 2001;97:1211–1218. - PubMed
-
- Schrappe M, Reiter A, Ludwig WD, et al. Improved outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia despite reduced use of anthracyclines and cranial radiotherapy: results of trial ALL-BFM 90. German-Austrian-Swiss ALL-BFM Study Group. Blood. 2000;95:3310–3322. - PubMed
-
- Pui CH, Sandlund JT, Pei D, et al. Improved outcome for children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of Total Therapy Study XIIIB at St Jude Children's Research Hospital. Blood. 2004;104:2690–2696. - PubMed
-
- Gaynon PS, Trigg ME, Heerema NA, et al. Children's Cancer Group trials in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: 1983-1995. Leukemia. 2000;14:2223–2233. - PubMed
-
- Silverman LB, Declerck L, Gelber RD, et al. Results of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Consortium protocols for children with newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia (1981-1995). Leukemia. 2000;14:2247–2256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

