Hyaluronidase expression induces prostate tumor metastasis in an orthotopic mouse model
- PMID: 17003496
- PMCID: PMC1698854
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.060324
Hyaluronidase expression induces prostate tumor metastasis in an orthotopic mouse model
Abstract
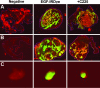
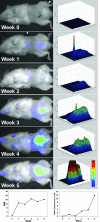
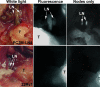
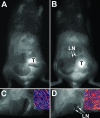
Molecular mechanisms of prostate cancer progression are frequently studied in mice by orthotopic injection of aggressive cell lines, which yield primary tumors that spontaneously metastasize to lymph nodes. In this report, we characterized the human prostate carcinoma cell line 22Rv1 in an orthotopic system and evaluated the functional relevance of the hyaluronidase Hyal1, a correlate of invasive human prostate cancer, to progression in this model. To provide real-time insights into these processes, we first validated use of an epidermal growth factor-conjugated fluorophore to illuminate orthotopic prostate tumors and their metastases in whole animal imaging. Animals receiving intraprostatic injections were tracked throughout a 6-week period. Tumor sizes were correlated 92% with total fluorescence intensities of 22 prostate tumors. In contrast to the highly tumorigenic and metastatic PC3M-LN4 cells, the 22Rv1 line was orthotopically tumorigenic but not metastatic, despite larger tumor sizes. Lymph node metastasis was successfully imaged in animals with PC3M-LN4 tumors on endpoint dissection. Stable transfection of 22Rv1 cells with Hyal1 did not alter growth kinetics of primary orthotopic tumors, but all animals implanted with Hyal1 transfectants exhibited tumor-positive para-aortic lymph nodes. Hyal1 is implicated as an inducer of prostate cancer metastatic progression.
Figures




References
-
- Pienta KJ, Smith DC. Advances in prostate cancer chemotherapy: a new era begins. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:300–323. - PubMed
-
- Cher ML. Mechanisms governing bone metastasis in prostate cancer. Curr Opin Urol. 2001;11:483–488. - PubMed
-
- Ekici S, Cerwinka WH, Duncan R, Gomez P, Civantos F, Soloway MS, Lokeshwar VB. Comparison of the prognostic potential of hyaluronic acid, hyaluronidase (HYAL-1), CD44v6 and microvessel density for prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 2004;112:121–129. - PubMed
-
- Lokeshwar VB, Cerwinka WH, Isoyama T, Lokeshwar BL. HYAL1 hyaluronidase in prostate cancer: a tumor promoter and suppressor. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7782–7789. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

