H-REV107-1 stimulates growth in non-small cell lung carcinomas via the activation of mitogenic signaling
- PMID: 17003497
- PMCID: PMC1698850
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.051341
H-REV107-1 stimulates growth in non-small cell lung carcinomas via the activation of mitogenic signaling
Abstract
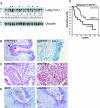
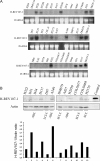
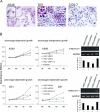
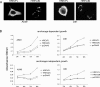
H-REV107-1, a known member of the class II tumor suppressor gene family, is involved in the regulation of differentiation and survival. We analyzed H-REV107-1 in non-small cell lung carcinomas, in normal lung, and in immortalized and tumor-derived cell lines. Sixty-eight percent of lung tumors revealed positive H-REV107-1-specific staining. Furthermore, survival analysis demonstrated a significant association of cytoplasmic H-REV107-1 with decreased patient survival. This suggested that H-REV107-1, known as a tumor suppressor, plays a different role in non-small cell lung carcinomas. Knock-down of H-REV107-1 expression in lung carcinoma cells inhibited anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent growth whereas overexpression of H-REV107-1 induced tumor cell proliferation. Consistent with results of the survival analysis, cytoplasmic localization of the protein was essential for this growth-inducing function. Analysis of signaling pathways potentially involved in this process demonstrated that overexpression of H-REV107-1 stimulated RAS-GTPase activity, ERK1,2 phosphorylation, and caveolin-1 expression in the cell lines analyzed. These results indicate that H-REV107-1 is deficient in its function as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung carcinomas and is required for proliferation and anchorage-independent growth in cells expressing high levels of the protein, thus contributing to tumor progression in a subset of non-small cell lung carcinomas.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The class II tumour suppressor gene H-REV107-1 is a target of interferon-regulatory factor-1 and is involved in IFNgamma-induced cell death in human ovarian carcinoma cells.Oncogene. 2002 Apr 25;21(18):2829-39. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205377. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 11973642
-
Phospholipase A/Acyltransferase enzyme activity of H-rev107 inhibits the H-RAS signaling pathway.J Biomed Sci. 2014 May 1;21(1):36. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-21-36. J Biomed Sci. 2014. PMID: 24884338 Free PMC article.
-
Growth-inhibitory activity and downregulation of the class II tumor-suppressor gene H-rev107 in tumor cell lines and experimental tumors.J Cell Biol. 1997 Feb 24;136(4):935-44. doi: 10.1083/jcb.136.4.935. J Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9049257 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional and translational downregulation of H-REV107, a class II tumour suppressor gene located on human chromosome 11q11-12.Oncogene. 1998 Sep 10;17(10):1305-12. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202060. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9771974
-
Induction of murine H-rev107 gene expression by growth arrest and histone acetylation: involvement of an Sp1/Sp3-binding GC-box.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 May 31;294(1):63-70. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00440-0. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. PMID: 12054741
Cited by
-
Pla2g16 phospholipase mediates gain-of-function activities of mutant p53.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jul 29;111(30):11145-50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404139111. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25024203 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of apoptosis by the retinoid inducible growth regulator RIG1 depends on the NC motif in HtTA cervical cancer cells.BMC Cell Biol. 2009 Feb 26;10:15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2121-10-15. BMC Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19245694 Free PMC article.
-
H-rev107 regulates prostaglandin D2 synthase-mediated suppression of cellular invasion in testicular cancer cells.J Biomed Sci. 2013 May 20;20(1):30. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-20-30. J Biomed Sci. 2013. PMID: 23687991 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting PLA2G16, a lipid metabolism gene, by Ginsenoside Compound K to suppress the malignant progression of colorectal cancer.J Adv Res. 2021 Jun 12;36:265-276. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.009. eCollection 2022 Feb. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35127176 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of PLA2G16 is associated with a better prognosis in HER2-positive breast cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2017 Apr;9(4):1002-1011. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2017.03.108. J Thorac Dis. 2017. PMID: 28523155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A, Ghafoor A, Ward E, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clin. 2003;53:5–26. - PubMed
-
- Huang SL, Shyu RY, Yeh MY, Jiang SY. Cloning and characterization of a novel retinoid-inducible gene 1(RIG1) deriving from human gastric cancer cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000;159:15–24. - PubMed
-
- Seftor RE, Seftor EA, Sheng S, Pemberton PA, Sager R, Hendrix MJ. Maspin suppresses the invasive phenotype of human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5681–5685. - PubMed
-
- Sers C, Husmann K, Nazarenko I, Reich S, Wiechen K, Zhumabayeva B, Adhikari P, Schroder K, Gontarewicz A, Schafer R. The class II tumour suppressor gene H-REV107-1 is a target of interferon-regulatory factor-1 and is involved in IFNgamma-induced cell death in human ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2002;21:2829–2839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

