Influence of endothelial cells on vascular smooth muscle cells phenotype after irradiation: implication in radiation-induced vascular damages
- PMID: 17003501
- PMCID: PMC1698856
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2006.060116
Influence of endothelial cells on vascular smooth muscle cells phenotype after irradiation: implication in radiation-induced vascular damages
Abstract
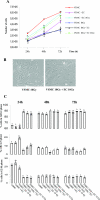
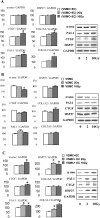
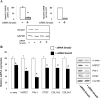
Damage to vessels is one of the most common effects of therapeutic irradiation on normal tissues. We undertook a study in patients treated with preoperative radiotherapy and demonstrated in vivo the importance of proliferation, migration, and fibrogenic phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) in radiation-induced vascular damage. These lesions may result from imbalance in the cross talk between endothelial cells (ECs) and VSMCs. Using co-culture models, we examined whether ECs influence proliferation, migration, and fibrogenic phenotype of VSMCs. In the presence of irradiated ECs, proliferation and migration of VSMCs were increased. Moreover, expressions of alpha-smooth muscle actin, connective tissue growth factor, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1, heat shock protein 27, and collagen type III, alpha 1 were up-regulated in VSMCs exposed to irradiated ECs. Secretion of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 was increased after irradiation of ECs, and irradiated ECs activated the Smad pathway in VSMCs by inducing Smad3/4 nuclear translocation and Smad-dependent promoter activation. Using small interferring RNA targeting Smad3 and a TGFbeta-RII neutralizing antibody, we demonstrate that a TGF-beta1/TGF-beta-RII/Smad3 pathway is involved in the fibrogenic phenotype of VSMCs induced by irradiated ECs. In conclusion, we show the importance of proliferation, migration, and fibrogenic phenotype of VSMCs in patients. Moreover, we demonstrate in vitro that ECs influence these fundamental mechanisms involved in radiation-induced vascular damages.
Figures






References
-
- Stone HB, Coleman CN, Anscher MS, McBride WH. Effects of radiation on normal tissue: consequences and mechanisms. Lancet Oncol. 2003;4:529–536. - PubMed
-
- Dorresteijn LD, Kappelle AC, Boogerd W, Klokman WJ, Balm AJ, Keus RB, van Leeuwen FE, Bartelink H. Increased risk of ischemic stroke after radiotherapy on the neck in patients younger than 60 years. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:282–288. - PubMed
-
- Molla M, Gironella M, Miquel R, Tovar V, Engel P, Biete A, Pique JM, Panes J. Relative roles of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in the pathogenesis of experimental radiation-induced intestinal inflammation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;57:264–273. - PubMed
-
- Panes J, Anderson DC, Miyasaka M, Granger DN. Role of leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion in radiation-induced microvascular dysfunction in rats. Gastroenterology. 1995;108:1761–1769. - PubMed
-
- Molla M, Gironella M, Salas A, Miquel R, Perez-del-Pulgar S, Conill C, Engel P, Biete A, Pique JM, Panes J. Role of P-selectin in radiation-induced intestinal inflammatory damage. Int J Cancer. 2001;96:99–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

