Regulation of cytotoxin expression by converging eukaryotic-type and two-component signalling mechanisms in Streptococcus agalactiae
- PMID: 17005013
- PMCID: PMC2593684
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05431.x
Regulation of cytotoxin expression by converging eukaryotic-type and two-component signalling mechanisms in Streptococcus agalactiae
Abstract
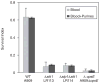
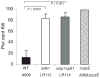
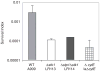
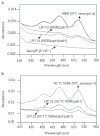
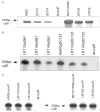
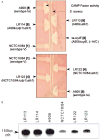
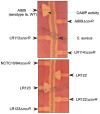
Signal transducing mechanisms are essential for regulation of gene expression in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms. Regulation of gene expression in eukaryotes is accomplished by serine/threonine and tyrosine kinases and cognate phosphatases. In contrast, gene expression in prokaryotes is controlled by two-component systems that comprise a sensor histidine kinase and a cognate DNA binding response regulator. Pathogenic bacteria utilize two-component systems to regulate expression of their virulence factors and for adaptive responses to the external environment. We have previously shown that the human pathogen Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B Streptococci, GBS) encodes a single eukaryotic-type serine/threonine kinase Stk1, which is important for virulence of the organism. In this study, we aimed to understand how Stk1 contributes to virulence of GBS. Our results indicate that Stk1 expression is important for resistance of GBS to human blood, neutrophils and oxidative stress. Consistent with these observations, Stk1 positively regulates transcription of a cytotoxin, beta-haemolysin/cytolysin (beta-H/C) that is critical for survival of GBS in the bloodstream and for resistance to oxidative stress. Interestingly, positive regulation of beta-H/C by Stk1 requires the two-component regulator CovR. Further, we show that Stk1 can negatively regulate transcription of CAMP factor in a CovR-dependent manner. As Stk1 phosphorylates CovR in vitro, these data suggest that serine/threonine phosphorylation impacts CovR-mediated regulation of GBS gene expression. In summary, our studies provide novel information that a eukaryotic-type serine/threonine kinase regulates two-component-mediated expression of GBS cytotoxins.
Figures
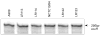
References
-
- Av-Gay Y, Everett M. The eukaryotic-like Ser/Thr protein kinases of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Trends Microbiol. 2000;8:238–244. - PubMed
-
- Baker CJ, Edwards MW. Group B streptococcal infections. In: Remington JS, Klein JO, editors. Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant. Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders; 1995. pp. 980–1054.
-
- Beier D, Gross R. Regulation of bacterial virulence by two-component systems. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2006;9:143–152. - PubMed
-
- Chaffin DO, Rubens CE. Blue/white screening of recombinant plasmids in Gram-positive bacteria by interruption of alkaline phosphatase gene (phoZ) expression. Gene. 1998;219:91–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

