Altered intercellular communication in lung fibroblast cultures from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 17005044
- PMCID: PMC1594576
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-122
Altered intercellular communication in lung fibroblast cultures from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Rationale: Gap junctions are membrane channels formed by an array of connexins which links adjacent cells realizing an electro- metabolic synapse. Connexin-mediated communication is crucial in the regulation of cell growth, differentiation, and development. The activation and proliferation of phenotypically altered fibroblasts are central events in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. We sought to evaluate the role of connexin-43, the most abundant gap-junction subunit in the human lung, in the pathogenesis of this condition.
Methods: We investigated the transcription and protein expression of connexin-43 and the gap-junctional intercellular communication (GJIC) in 5 primary lung fibroblast lines derived from normal subjects (NF) and from 3 histologically proven IPF patients (FF).
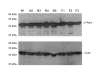
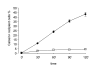
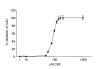
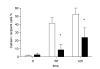
Results: Here we show that connexin-43 mRNA was significantly reduced in FF as demonstrated by standard and quantitative RT-PCR. GJIC was functionally evaluated by means of flow-cytometry. In order to demonstrate that dye spreading was taking place through gap junctions, we used carbenoxolone as a pharmacological gap-junction blocker. Carbenoxolone specifically blocked GJIC in our system in a concentration dependent manner. FF showed a significantly reduced homologous GJIC compared to NF. Similarly, GJIC was significantly impaired in FF when a heterologous NF line was used as dye donor, suggesting a complete defect in GJIC of FF.
Conclusion: These results suggest a novel alteration in primary lung fibroblasts from IPF patients. The reduced Cx43 expression and the associated alteration in cell-to-cell communication may justify some of the known pathological characteristic of this devastating disease that still represents a challenge to the medical practice.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibition of gap junction-mediated intercellular communication by TNF-alpha in cultured human corneal fibroblasts.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Apr;46(4):1195-200. doi: 10.1167/iovs.04-0840. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 15790879
-
Modulation of homologous gap junctional intercellular communication of human dermal fibroblasts via a paracrine factor(s) generated by squamous tumor cells.Carcinogenesis. 2003 Nov;24(11):1737-48. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgg153. Epub 2003 Aug 29. Carcinogenesis. 2003. PMID: 12949050
-
Connexin expression and functional analysis of gap junctional communication in mouse embryonic stem cells.Stem Cells. 2008 Feb;26(2):431-9. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.2007-0482. Epub 2007 Nov 29. Stem Cells. 2008. PMID: 18055446
-
Phosphorylation of connexin43 induced by Src: regulation of gap junctional communication between transformed cells.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Dec 10;313(20):4083-90. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.09.010. Epub 2007 Sep 20. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17956757 Review.
-
Gap junctions in the ovary: expression, localization and function.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008 Jan 30;282(1-2):18-25. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2007.11.001. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18162286 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperoxia arrests pulmonary development in newborn rats via disruption of endothelial tight junctions and downregulation of Cx40.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Jul;10(1):61-7. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2192. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 24789212 Free PMC article.
-
Alveolar epithelial disintegrity in pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Aug 1;311(2):L185-91. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00115.2016. Epub 2016 May 27. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27233996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis on clinical outcomes of lung cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 15;11(1):8312. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87747-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33859288 Free PMC article.
-
Airborne PAHs inhibit gap junctional intercellular communication and activate MAPKs in human bronchial epithelial cell line.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;79:103422. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2020.103422. Epub 2020 May 31. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32492535 Free PMC article.
-
Common pathways in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and cancer.Eur Respir Rev. 2013 Sep 1;22(129):265-72. doi: 10.1183/09059180.00003613. Eur Respir Rev. 2013. PMID: 23997054 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Selman M, King TE, Pardo A. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy. Ann Intern Med. 2001;134:136–151. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn CIII, Boldt J, King TEJ, Crouch E, Vartio T, McDonald JA. An immunohistochemical study of architectural remodeling and connective tissue synthesis in pulmonary fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989;140:1693–1703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

