Genomic heterogeneity in the density of noncoding single-nucleotide and microsatellite polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 17005334
- PMCID: PMC2593462
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gene.2006.07.026
Genomic heterogeneity in the density of noncoding single-nucleotide and microsatellite polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
The density and distribution of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) across the genome has important implications for linkage disequilibrium mapping and association studies, and the level of simple-sequence microsatellite polymorphisms has important implications for the use of oligonucleotide hybridization methods to genotype SNPs. To assess the density of these types of polymorphisms in P. falciparum, we sampled introns and noncoding DNA upstream and downstream of coding regions among a variety of geographically diverse parasites. Across 36,229 base pairs of noncoding sequence representing 41 genetic loci, a total of 307 polymorphisms including 248 polymorphic microsatellites and 39 SNPs were identified. We found a significant excess of microsatellite polymorphisms having a repeat unit length of one or two, compared to those with longer repeat lengths, as well as a nonrandom distribution of SNP polymorphisms. Almost half of the SNPs localized to only three of the 41 genetic loci sampled. Furthermore, we find significant differences in the frequency of polymorphisms across the two chromosomes (2 and 3) examined most extensively, with an excess of SNPs and a surplus of polymorphic microsatellites on chromosome 3 as compared to chromosome 2 (P=0.0001). Furthermore, at some individual genetic loci we also find a nonrandom distribution of polymorphisms between coding and flanking noncoding sequences, where completely monomorphic regions may flank highly polymorphic genes. These data, combined with our previous findings of nonrandom distribution of SNPs across chromosome 2, suggest that the Plasmodium falciparum genome may be a mosaic with regard to genetic diversity, containing chromosomal regions that are highly polymorphic interspersed with regions that are much less polymorphic.
Figures
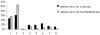
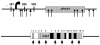
References
-
- Barry AE, Leliwa A, Choi M, Nielsen KM, Hartl DL, Day KP. DNA sequence artifacts and the estimation of time to the most recent common ancestor (TMRCA) of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2003;130:143–147. - PubMed
-
- Barry AE, et al. Variable SNP density in aspartyl-protease genes of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Gene. 2006;376:163–173. - PubMed
-
- Biswas S, Escalante A, Chaiyaroj S, Angkasekwinai P, Lal AA. Prevalence of point mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase and dihydropteroate synthetase genes of Plasmodium falciparum isolates from India and Thailand: a molecular epidemiologic study. Trop Med Int Health. 2000;5:737–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

