Muscle cell and motor protein function in patients with a IIa myosin missense mutation (Glu-706 to Lys)
- PMID: 17005402
- PMCID: PMC1693964
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmd.2006.07.023
Muscle cell and motor protein function in patients with a IIa myosin missense mutation (Glu-706 to Lys)
Abstract
The pathogenic events leading to the progressive muscle weakness in patients with a E706K mutation in the head of the myosin heavy chain (MyHC) IIa were analyzed at the muscle cell and motor protein levels. Contractile properties were measured in single muscle fiber segments using the skinned fiber preparation and a single muscle fiber in vitro motility assay. A dramatic impairment in the function of the IIa MyHC isoform was observed at the motor protein level. At the single muscle fiber level, on the other hand, a general decrease was observed in the number of preparations where the specific criteria for acceptance were fulfilled irrespective of MyHC isoform expression. Our results provide evidence that the pathogenesis of the MyHC IIa E706K myopathy involves defective function of the mutated myosin as well as alterations in the structural integrity of all muscle cells irrespective of MyHC isoform expression.
Figures


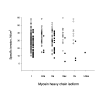
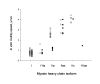
References
-
- Schiaffino S, Reggiani C. Molecular diversity of myofibrillar proteins: gene regulation and functional significance. Physiol Rev. 1996;76(2):371–423. - PubMed
-
- Pette D, Staron RS. Transitions of muscle fiber phenotypic profiles. Histochem Cell Biol. 2001;115(5):359–372. - PubMed
-
- Shrager JB, Desjardins PR, Burkman JM, Konig SK, Stewart SK, Su L, et al. Human skeletal myosin heavy chain genes are tightly linked in the order embryonic-IIa-IId/x-ILb-perinatal-extraocular [In Process Citation] J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2000;21(4):345–355. - PubMed
-
- Larsson L, Li X, Edstrom L, Eriksson LI, Zackrisson H, Argentini C, et al. Acute quadriplegia and loss of muscle myosin in patients treated with nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents and corticosteroids: mechanisms at the cellular and molecular levels [see comments] Crit Care Med. 2000;28(1):34–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

