Growth transformation of human T cells by herpesvirus saimiri requires multiple Tip-Lck interaction motifs
- PMID: 17005671
- PMCID: PMC1617286
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01112-06
Growth transformation of human T cells by herpesvirus saimiri requires multiple Tip-Lck interaction motifs
Abstract
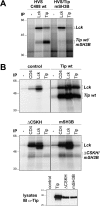
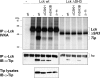
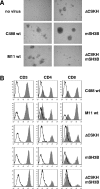
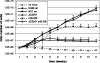
Lymphoma induction and T-cell transformation by herpesvirus saimiri strain C488 depends on two viral oncoproteins, StpC and Tip. The major interaction partner of Tip is the protein tyrosine kinase Lck, a key regulator of T-cell activation. The Lck binding domain (LBD) of Tip comprises two interaction motifs, a proline-rich SH3 domain-binding sequence (SH3B) and a region with homology to the C terminus of Src family kinase domains (CSKH). In addition, biophysical binding analyses with purified Lck-SH2 domain suggest the phosphorylated tyrosine residue 127 of Tip (pY127) as a potential third Lck interaction site. Here, we addressed the relevance of the individual binding motifs, SH3B, CSKH, and pY127, for Tip-Lck interaction and for human T-cell transformation. Both motifs within the LBD displayed Lck binding activities and cooperated to achieve a highly efficient interaction, while pY127, the major tyrosine phosphorylation site of Tip, did not enhance Lck binding in T cells. Herpesvirus saimiri strain C488 recombinants lacking one or both LBD motifs of Tip lost their transforming potential on human cord blood lymphocytes. Recombinant virus expressing Tip with a mutation at position Y127 was still able to transform human T lymphocytes but, in contrast to wild-type virus, was strictly dependent on exogenous interleukin-2. Thus, the strong Lck binding mediated by cooperation of both LBD motifs was essential for the transformation of human T cells by herpesvirus saimiri C488. The major tyrosine phosphorylation site Y127 of Tip was particularly required for transformation in the absence of exogenous interleukin-2, suggesting its involvement in cytokine signaling pathways.
Figures


References
-
- Bauer, F., E. Hofinger, S. Hoffmann, P. Rösch, K. Schweimer, and H. Sticht. 2004. Characterization of Lck-binding elements in the herpesviral regulatory Tip protein. Biochemistry 43:14932-14939. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

