Vaccinia virus infection attenuates innate immune responses and antigen presentation by epidermal dendritic cells
- PMID: 17005676
- PMCID: PMC1617288
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00354-06
Vaccinia virus infection attenuates innate immune responses and antigen presentation by epidermal dendritic cells
Abstract
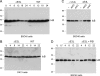
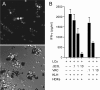
Langerhans cells (LCs) are antigen-presenting cells in the skin that play sentinel roles in host immune defense by secreting proinflammatory molecules and activating T cells. Here we studied the interaction of vaccinia virus with XS52 cells, a murine epidermis-derived dendritic cell line that serves as a surrogate model for LCs. We found that vaccinia virus productively infects XS52 cells, yet this infection displays an atypical response to anti-poxvirus agents. Whereas adenosine N1-oxide blocked virus production and viral protein synthesis during a synchronous infection, cytosine arabinoside had no effect at concentrations sufficient to prevent virus replication in BSC40 monkey kidney cells. Vaccinia virus infection of XS52 cells not only failed to elicit the production of various cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), IL-6, IL-10, IL-12 p40, alpha interferon (IFN-alpha), and IFN-gamma, it actively inhibited the production of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-6 by XS52 cells in response to exogenous lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or poly(I:C). Infection with a vaccinia virus mutant lacking the E3L gene resulted in TNF-alpha secretion in the absence of applied stimuli. Infection of XS52 cells or BSC40 cells with the DeltaE3L virus, but not wild-type vaccinia virus, triggered proteolytic decay of IkappaBalpha. These results suggest a novel role for the E3L protein as an antagonist of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. DeltaE3L-infected XS52 cells secreted higher levels of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in response to LPS and poly(I:C) than did cells infected with the wild-type virus. XS52 cells were productively infected by a vaccinia virus mutant lacking the K1L gene. DeltaK1L-infected cells secreted higher levels of TNF-alpha and IL-6 in response to LPS than wild-type virus-infected cells. Vaccinia virus infection of primary LCs harvested from mouse epidermis was nonpermissive, although a viral reporter protein was expressed in the infected LCs. Vaccinia virus infection of primary LCs strongly inhibited their capacity for antigen-specific activation of T cells. Our results highlight suppression of the skin immune response as a feature of orthopoxvirus infection.
Figures

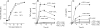
References
-
- Akira, S., S. Uematsu, and O. Takeuchi. 2006. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124:783-801. - PubMed
-
- Allan, R. S., C. M. Smith, G. T. Belz, A. L. van Lint, L. M. Wakim, W. R. Heath, and F. R. Carbone. 2003. Epidermal viral immunity induced by CD8α+ dendritic cells but not by Langerhans cells. Science 301:1925-1928. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau, J., and R. M. Steinman. 1998. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392:245-252. - PubMed
-
- Berthier-Vergnes, O., F. Bermond, V. Flacher, C. Massacrier, D. Schmitt, and J. Peguet-Navarro. 2005. TNF-α enhances phenotypic and functional maturation of human epidermal Langerhans cells and induces IL-12 p40 and IP-10/CXCL-10 production. FEBS Lett. 579:3660-3668. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

