Human cytomegalovirus UL84 protein contains two nuclear export signals and shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm
- PMID: 17005707
- PMCID: PMC1617278
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00995-06
Human cytomegalovirus UL84 protein contains two nuclear export signals and shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm
Abstract
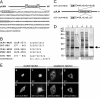
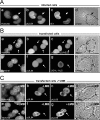
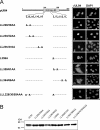
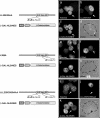
Previous studies defined pUL84 of human cytomegalovirus as an essential regulatory protein with nuclear localization that was proposed to act during initiation of viral-DNA synthesis. Recently, we demonstrated that a complex domain of 282 amino acids within pUL84 functions as a nonconventional nuclear localization signal. Sequence inspection of this domain revealed the presence of motifs with homology to leucine-rich nuclear export signals. Here, we report the identification of two functional, autonomous nuclear export signals and show that pUL84 acts as a CRM-1-dependent nucleocytoplasmic shuttling protein. This suggests an unexpected cytoplasmic role for this essential viral regulatory protein.
Figures
References
-
- Boehmer, P. E., M. S. Dodson, and I. R. Lehman. 1993. The herpes simplex virus type-1 origin binding protein. DNA helicase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 268:1220-1225. - PubMed
-
- Bruckner, R. C., J. J. Crute, M. S. Dodson, and I. R. Lehman. 1991. The herpes simplex virus 1 origin binding protein: a DNA helicase. J. Biol. Chem. 266:2669-2674. - PubMed
-
- Colletti, K. S., Y. Xu, I. Yamboliev, and G. S. Pari. 2005. Human cytomegalovirus UL84 is a phosphoprotein that exhibits UTPase activity and is a putative member of the DExD/H box family of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 280:11955-11960. - PubMed
-
- Dodson, M. S., and I. R. Lehman. 1993. The herpes simplex virus type I origin binding protein. DNA-dependent nucleoside triphosphatase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 268:1213-1219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

