A purified Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein with therapeutic activity against the hookworm parasite Ancylostoma ceylanicum
- PMID: 17005719
- PMCID: PMC1622792
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0607002103
A purified Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein with therapeutic activity against the hookworm parasite Ancylostoma ceylanicum
Abstract
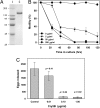
Crystal (Cry) proteins produced by the soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) are harmless to vertebrates, but they are highly toxic to insects and nematodes. Their value in controlling insects that destroy crops and transmit human diseases is well established. Although it has recently been demonstrated that a few individual Bt Cry proteins, such as Cry5B, are toxic to a wide range of free-living nematodes, the potential activity of purified Cry proteins against parasitic nematodes remains largely unknown. We report here studies aimed at characterizing in vitro and in vivo anthelminthic activities of purified recombinant Cry5B against the hookworm parasite Ancylostoma ceylanicum, a bloodfeeding gastrointestinal nematode for which humans are permissive hosts. By using in vitro larval development assays, Cry5B was found to be highly toxic to early stage hookworm larvae. Exposure of adult A. ceylanicum to Cry5B was also associated with significant toxicity, including a substantial reduction in egg excretion by adult female worms. To demonstrate therapeutic efficacy in vivo, hamsters infected with A. ceylanicum were treated with three daily oral doses of purified Cry5B, the benzimidazole anthelminthic mebendazole, or buffer. Compared with control (buffer-treated) animals, infected hamsters that received Cry5B showed statistically significant improvements in growth and blood hemoglobin levels as well as reduced worm burdens that were comparable to the mebendazole-treated animals. These data demonstrate that Cry5B is highly active in vitro and in vivo against a globally significant nematode parasite and that Cry5B warrants further clinical development for human and veterinary use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bacillus thuringiensis Cry5B protein as a new pan-hookworm cure.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2018 Aug;8(2):287-294. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 4. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 29772478 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic and single-dose in vivo therapeutic studies of Cry5B anthelmintic action against hookworms.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(11):e1900. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001900. Epub 2012 Nov 8. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012. PMID: 23145203 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo and in vitro studies of Cry5B and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist anthelmintics reveal a powerful and unique combination therapy against intestinal nematode parasites.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 May 18;12(5):e0006506. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006506. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29775454 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial pore-forming proteins as anthelmintics.Invert Neurosci. 2012 Jun;12(1):37-41. doi: 10.1007/s10158-012-0135-8. Epub 2012 May 5. Invert Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22562659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ancylostoma ceylanicum, a re-emerging but neglected parasitic zoonosis.Int J Parasitol. 2013 Nov;43(12-13):1009-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2013.07.006. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Int J Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23968813 Review.
Cited by
-
The theoretical 3D structure of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry5Ba.J Mol Model. 2008 Sep;14(9):843-8. doi: 10.1007/s00894-008-0318-8. Epub 2008 May 27. J Mol Model. 2008. PMID: 18504623
-
Intracellular and Extracellular Expression of Bacillus thuringiensis Crystal Protein Cry5B in Lactococcus lactis for Use as an Anthelminthic.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015 Dec 18;82(4):1286-94. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02365-15. Print 2016 Feb 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26682852 Free PMC article.
-
Twenty-first century progress toward the global control of human hookworm infection.Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2011 Jun;13(3):210-7. doi: 10.1007/s11908-011-0182-z. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2011. PMID: 21462001
-
Comparison of percutaneous vs oral infection of hamsters with the hookworm Ancylostoma ceylanicum: Parasite development, pathology and primary immune response.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022 Jan 5;16(1):e0010098. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010098. eCollection 2022 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022. PMID: 34986139 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient and Scalable Process to Produce Novel and Highly Bioactive Purified Cytosolic Crystals from Bacillus thuringiensis.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0235622. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02356-22. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35946940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crompton DW, Engels D, Montresor A, Neira MP, Savioli L. Acta Trop. 2003;86:121–124. - PubMed
-
- de Silva NR, Brooker S, Hotez PJ, Montresor A, Engels D, Savioli L. Trends Parasitol. 2003;19:547–551. - PubMed
-
- Coles GC. Res Vet Sci. 2005;78:99–108. - PubMed
-
- Chandrawathani P, Waller PJ, Adnan M, Hoglund J. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2003;35:17–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

