Phaeoacremonium krajdenii, a cause of white grain eumycetoma
- PMID: 17005754
- PMCID: PMC1698411
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01019-06
Phaeoacremonium krajdenii, a cause of white grain eumycetoma
Abstract
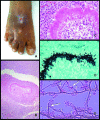
We describe the first case of white grain pedal eumycetoma caused by Phaeoacremonium krajdenii in a 41-year-old man from Goa, India. Based on histological examination of biopsy tissue showing serpentine granules, a culture of the granules yielding phaeoid fungal colonies, and morphological characteristics and sequence comparison of the partial beta-tubulin gene with the ex-type isolate of P. krajdenii, the causal agent was identified as P. krajdenii.
Figures
References
-
- Albornoz, M. B. 1974. Cephalosporium serrae, agente etiologico de micetomas. Mycopathol. Mycol. Appl. 54:485-498. - PubMed
-
- Chandler, F. W., and J. C. Watts. 1987. Pathologic diagnosis of fungal infections, p. 251-263. American Society of Clinical Pathologists Press, Chicago, Ill.
-
- Crous, P. W., W. Gams, M. J. Wingfield, and P. S. Van Wyk. 1996. Phaeoacremonium gen. nov. associated with wilt and decline disease of woody hosts and human infections. Mycologia 88:786-796.
-
- Dupont, J., S. Magnim, C. Césari, and M. Gatica. 2002. ITS and β-tubulin markers help delineate Phaeoacremonium species, and the occurrence of P. parasiticum in grapevine disease in Argentina. Mycol. Res. 106:1143-1150.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

