Novel robust hepatitis C virus mouse efficacy model
- PMID: 17005803
- PMCID: PMC1610068
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00413-06
Novel robust hepatitis C virus mouse efficacy model
Abstract
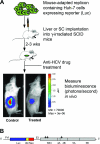
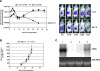
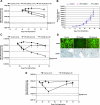
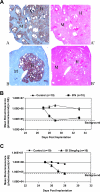
The lack of a robust small-animal model for hepatitis C virus (HCV) has hindered the discovery and development of novel drug treatments for HCV infections. We developed a reproducible and easily accessible xenograft mouse efficacy model in which HCV RNA replication is accurately monitored in vivo by real-time, noninvasive whole-body imaging of gamma-irradiated SCID mice implanted with a mouse-adapted luciferase replicon-containing Huh-7 cell line (T7-11). The model was validated by demonstrating that both a small-molecule NS3/4A protease inhibitor (BILN 2061) and human alpha interferon (IFN-alpha) decreased HCV RNA replication and that treatment withdrawal resulted in a rebound in replication, which paralleled clinical outcomes in humans. We further showed that protease inhibitor and IFN-alpha combination therapy was more effective in reducing HCV RNA replication than treatment with each compound alone and supports testing in humans. This robust mouse efficacy model provides a powerful tool for rapid evaluation of potential anti-HCV compounds in vivo as part of aggressive drug discovery efforts.
Figures

References
-
- Alter, H. J., and L. B. Seeff. 2000. Recovery, persistence, and sequelae in hepatitis C virus infection: a perspective on long-term outcome. Semin. Liver Dis. 20:17-35. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. 1999. Global surveillance and control of hepatitis C. Report of a WHO consultation organized in collaboration with the Viral Hepatitis Prevention Board, Antwerp, Belgium. J. Viral Hepat. 6:35-47. - PubMed
-
- Bartenschlager, R., M. Frese, and T. Pietschmann. 2004. Novel insights into hepatitis C virus replication and persistence. Adv. Virus Res. 63:71-180. - PubMed
-
- Bartenschlager, R., A. Kaul, and S. Sparacio. 2003. Replication of the hepatitis C virus in cell culture. Antiviral Res. 60:91-102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

