Mycobacterium leprae is naturally resistant to PA-824
- PMID: 17005816
- PMCID: PMC1610092
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00488-06
Mycobacterium leprae is naturally resistant to PA-824
Abstract
Leprosy responds very slowly to the current multidrug therapy, and hence there is a need for novel drugs with potent bactericidal activity. PA-824 is a 4-nitroimidazo-oxazine that is currently undergoing phase I clinical trials for the treatment of tuberculosis. The activity of PA-824 against Mycobacterium leprae was tested and compared with that of rifampin in axenic cultures, macrophages, and two different animal models. Our results conclusively demonstrate that PA-824 has no effect on the viability of M. leprae in all three models, consistent with the lack of the nitroimidazo-oxazine-specific nitroreductase, encoded by Rv3547 in the M. leprae genome, which is essential for activation of this molecule.
Figures
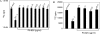
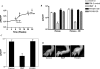
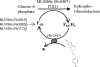
References
-
- Baker, W. R., C. Shaopei, and E. L. Keeler. September. 1997. Nitroimidazole antibacterial compounds and methods of use thereof. U.S. patent 5,668,127.
-
- Barry, C. E., III, H. I. Boshoff, and C. S. Dowd. 2004. Prospects for clinical introduction of nitroimidazole antibiotics for the treatment of tuberculosis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 10:3239-3262. - PubMed
-
- Camus, J. C., M. J. Pryor, C. Medigue, and S. T. Cole. 2002. Re-annotation of the genome sequence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv. Microbiology 148:2967-2973. - PubMed
-
- Cellona, R. V., M. F. Balagon, E. C. dela Cruz, J. A. Burgos, R. M. Abalos, G. P. Walsh, R. Topolski, R. H. Gelber, and D. S. Walsh. 2003. Long-term efficacy of 2 year WHO multiple drug therapy (MDT) in multibacillary (MB) leprosy patients. Int. J. Lepr. Other Mycobact. Dis. 71:308-319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

