A ubiquitin ligase complex assembles linear polyubiquitin chains
- PMID: 17006537
- PMCID: PMC1618115
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601360
A ubiquitin ligase complex assembles linear polyubiquitin chains
Abstract
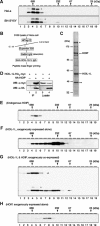
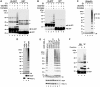
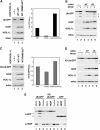
The ubiquitin system plays important roles in the regulation of numerous cellular processes by conjugating ubiquitin to target proteins. In most cases, conjugation of polyubiquitin to target proteins regulates their function. In the polyubiquitin chains reported to date, ubiquitin monomers are linked via isopeptide bonds between an internal Lys and a C-terminal Gly. Here, we report that a protein complex consisting of two RING finger proteins, HOIL-1L and HOIP, exhibits ubiquitin polymerization activity by recognizing ubiquitin moieties of proteins. The polyubiquitin chain generated by the complex is not formed by Lys linkages, but by linkages between the C- and N-termini of ubiquitin, indicating that the ligase complex possesses a unique feature to assemble a novel head-to-tail linear polyubiquitin chain. Moreover, the complex regulates the stability of Ub-GFP (a GFP fusion protein with an N-terminal ubiquitin). The linear polyubiquitin chain generated post-translationally may function as a new modulator of proteins.
Figures

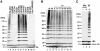

References
-
- Bayle J, Lopez S, Iwai K, Dubreuil P, De Sepulveda P (2006) The E3 ubiquitin ligase HOIL-1 induces the polyubiquitination and degradation of SOCS6 associated proteins. FEBS Lett 580: 2609–2614 - PubMed
-
- Ben-Saadon R, Fajerman I, Ziv T, Hellman U, Schwartz AL, Ciechanover A (2004) The tumor suppressor protein p16(INK4a) and the human papillomavirus oncoprotein-58 E7 are naturally occurring lysine-less proteins that are degraded by the ubiquitin system. Direct evidence for ubiquitination at the N-terminal residue. J Biol Chem 279: 41414–41421 - PubMed
-
- Bertolaet BL, Clarke DJ, Wolff M, Watson MH, Henze M, Divita G, Reed SI (2001) UBA domains of DNA damage-inducible proteins interact with ubiquitin. Nat Struct Biol 8: 417–422 - PubMed
-
- Bloom J, Amador V, Bartolini F, DeMartino G, Pagano M (2003) Proteasome-mediated degradation of p21 via N-terminal ubiquitinylation. Cell 115: 71–82 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

