Anion channels in astrocytes: biophysics, pharmacology, and function
- PMID: 17006903
- PMCID: PMC2556042
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.20423
Anion channels in astrocytes: biophysics, pharmacology, and function
Abstract
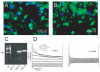
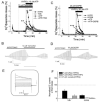
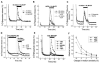
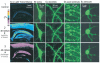
The chloride/anion channels that have been so far identified in cultured astrocytes and those that have been confirmed in situ by a combination of mRNA identification, immunocytochemistry, and biophysical studies are reviewed. It is emphasized that we are just beginning to describe such channels and analyze their functions in astrocytes. The best-studied anion channels studied so far are those known as volume-regulated anion channels (VRACs). These, as for most channels, have been mainly studied in cultured astrocytes, but some correlative studies have been done in situ, because these channels have been emphasized as release routes for transmitters; namely, excitatory amino acids and ATP. They are activated by cell shape changes and cell swelling, and the release of amino acids and ATP and chloride currents, measured by whole cell clamping, by these processes has been well described, as is also their activation by low concentrations of extracellular ATP. However, the identity of these channels in astrocytes, as in all other cells, remains elusive. The potential involvement of VRACs in pathological states such as stroke, metastasis, and spreading depression is also discussed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased release of excitatory amino acids by the actions of ATP and peroxynitrite on volume-regulated anion channels (VRACs) in astrocytes.Neurochem Int. 2004 Sep;45(4):511-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2003.11.002. Neurochem Int. 2004. PMID: 15186917
-
Pharmacological comparison of swelling-activated excitatory amino acid release and Cl- currents in cultured rat astrocytes.J Physiol. 2006 May 1;572(Pt 3):677-89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.103820. J Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16527858 Free PMC article.
-
ATP potently modulates anion channel-mediated excitatory amino acid release from cultured astrocytes.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002 Aug;283(2):C569-78. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00438.2001. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12107067
-
VRACs CARVe a path for novel mechanisms of communication in the CNS.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):pe42. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006pe42. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047222 Review.
-
ATP release through pannexon channels.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015 Jul 5;370(1672):20140191. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0191. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26009770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Persistent astroglial swelling accompanies rapid reversible dendritic injury during stroke-induced spreading depolarizations.Glia. 2012 Nov;60(11):1709-20. doi: 10.1002/glia.22390. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Glia. 2012. PMID: 22821441 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytic modulation of potassium under seizures.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Jun;15(6):980-987. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.270295. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31823867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensing and regulation of cell volume - we know so much and yet understand so little: TRPV4 as a sensor of volume changes but possibly without a volume-regulatory role?Channels (Austin). 2018 Jan 1;12(1):100-108. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2018.1438009. Channels (Austin). 2018. PMID: 29424275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical role of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) in astrocytic Ca2+ signaling events elicited by cerebral edema.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 11;108(2):846-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015217108. Epub 2010 Dec 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21187412 Free PMC article.
-
Dual regulation of Ca2+-dependent glutamate release from astrocytes: vesicular glutamate transporters and cytosolic glutamate levels.Glia. 2009 Sep;57(12):1296-305. doi: 10.1002/glia.20849. Glia. 2009. PMID: 19191347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agnel M, Vermat T, Culouscou JM. Identification of three novel members of the calcium-dependent chloride channel (CaCC) family predominantly expressed in the digestive tract and trachea. FEBS Lett. 1999;455:295–301. - PubMed
-
- Aitken PG, Borgdorff AJ, Juta AJA, Kiehart DP, Somjen GG, Wadman WJ. Volume changes induced by osmotic stress in freshly isolated rat hippocampal neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1998;436:991–998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

