Improved method of plasma 8-Isoprostane measurement and association analyses with habitual drinking and smoking
- PMID: 17007051
- PMCID: PMC4100666
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i36.5846
Improved method of plasma 8-Isoprostane measurement and association analyses with habitual drinking and smoking
Abstract
Aim: To develop a simple and accurate method for quantifying 8-isoprostane in plasma by employing a combination of two-step solid-phase extraction of samples and a commercially available ELISA kit, and by this method to examine the effects of drinking and smoking habits against the levels of plasma 8-isoprostane in healthy Japanese volunteers.
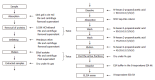
Methods: Plasma 8-isoprostane was extracted with ODS gel suspension followed by NH(2) Sep-Pak column. The 8-isoprostane fractions were assayed using a commercially available ELISA kit. We measured plasma 8-isoprostane levels in 157 healthy Japanese volunteers divided into three groups (64 non-habitual drinkers, 56 moderate drinkers and 37 habitual drinkers) according to their alcohol consumption per week. Genotypes of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) were also determined to investigate the plasma 8-isoprostane levels with reference to drinking habits. In addition, the plasma 8-isoprostane levels of 96 non-smokers and 61 smokers from the same subjects were compared.
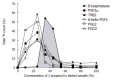
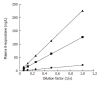
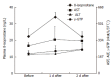
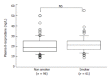
Results: Our method fulfilled all the requirements for use in routine clinical assays with respect to sensitivity, intra- and inter-assay reproducibility, accuracy and dynamic assay range. Significant increases of plasma 8-isoprostane levels were observed in female habitual drinkers when compared with those of non-habitual drinkers (t = 5.494, P<0.0001) as well as moderate drinkers (t = 3.542, P<0.005), and 8-isoprostane levels were also significantly different between ALDH2*2/1 and ALDH2*1/1 in the female habitual drinkers (t = 6.930, P<0.0001), suggesting that excessive drinking of alcohol may increase oxidization stress, especially in females. On the contrary, no significant difference of the plasma 8-isoprostane levels was observed between non-smokers and smokers.
Conclusion: Our present method was proved to be a simple and accurate tool for measuring plasma 8-isoprostane. However, the clinical utility of plasma 8-isoprostane for drinking and smoking habits was limited since elevated 8-isoprostane levels were observed in female heavy drinkers, and no association was found between smokers and nonsmokers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[An association between plasma levels of 8-isoprostane and alcohol drinking habits in Japanese volunteers].Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2004 Apr;39(2):105-17. Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15160889 Japanese.
-
Biological markers of alcoholism with respect to genotypes of low-Km aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH2) in Japanese subjects.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000 Apr;24(4 Suppl):30S-33S. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2000. PMID: 10803776
-
Associations of alcohol drinking and cigarette smoking with serum lipid levels in healthy middle-aged men.Alcohol Alcohol. 2008 May-Jun;43(3):274-80. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agn005. Epub 2008 Feb 18. Alcohol Alcohol. 2008. PMID: 18283096
-
Age-dependent associations of smoking and drinking with non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.Metabolism. 2010 Jul;59(7):1074-81. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.11.004. Epub 2009 Dec 31. Metabolism. 2010. PMID: 20045152
-
[Red blood cell deformability in relation to gender, age, blood pressure, obesity, serum lipids, alcohol consumption and smoking].Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2003 May;58(2):287-97. doi: 10.1265/jjh.58.287. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 12806968 Japanese.
Cited by
-
Salivary lactate and 8-isoprostaglandin F2α as potential non-invasive biomarkers for monitoring heart failure: a pilot study.Sci Rep. 2020 May 4;10(1):7441. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64112-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32366899 Free PMC article.
-
Application of medical and analytical methods in Lyme borreliosis monitoring.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012 Mar;402(7):2233-48. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5451-z. Epub 2011 Oct 21. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22015476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional significance of 8-isoprostanes in sinonasal disease and asthma.Respir Med. 2021 Aug-Sep;185:106506. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106506. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 34166960 Free PMC article.
-
Carotenoids and Markers of Oxidative Stress in Human Observational Studies and Intervention Trials: Implications for Chronic Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Jun 17;8(6):179. doi: 10.3390/antiox8060179. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31213029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early diagnosis of oral submucous fibrosis using salivary 8-OHDG and 8-Isoprostane.Bioinformation. 2024 Sep 30;20(9):1042-1045. doi: 10.6026/9732063002001042. eCollection 2024. Bioinformation. 2024. PMID: 39917199 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belli R, Amerio P, Brunetti L, Orlando G, Toto P, Proietto G, Vacca M, Tulli A. Elevated 8-isoprostane levels in basal cell carcinoma and in UVA irradiated skin. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2005;18:497–502. - PubMed
-
- Schwedhelm E, Böger RH. Application of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for analysis of isoprostanes: their role in cardiovascular disease. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2003;41:1552–1561. - PubMed
-
- Chehne F, Oguogho A, Lupattelli G, Budinsky AC, Palumbo B, Sinzinger H. Increase of isoprostane 8-epi-PGF(2alpha)after restarting smoking. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2001;64:307–310. - PubMed
-
- Ohashi N, Yoshikawa M. Rapid and sensitive quantification of 8-isoprostaglandin F2alpha in human plasma and urine by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2000;746:17–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

