Oral fluid as an alternative matrix to monitor opiate and cocaine use in substance-abuse treatment patients
- PMID: 17008030
- PMCID: PMC1892788
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.08.020
Oral fluid as an alternative matrix to monitor opiate and cocaine use in substance-abuse treatment patients
Abstract
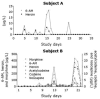
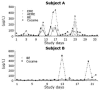
Interest in oral fluid as an alternative matrix for monitoring drug use is due to its ease-of-collection and non-invasiveness; however, limited data are available on the disposition of drugs into oral fluid. The objective of this research was to provide data on the presence and concentrations of heroin, cocaine and multiple metabolites in oral fluid after illicit opioid and cocaine use. Thrice weekly oral fluid specimens (N=403) from 16 pregnant opiate-dependent women were obtained with the Salivette oral fluid collection device. Evidence of heroin (N=62) and cocaine (N=130) use was detected in oral fluid by LC-APCI-MS/MS. 6-Acetylmorphine (6-AM), heroin and morphine were the major opiates detected, with median concentrations of 5.2, 2.3, and 7.5 microg/L, respectively. Cocaine and benzoylecgonine (BE) had median concentrations of 6.4 and 3.4 microg/L. Application of the Substance Abuse Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) recommended cutoffs for morphine and codeine (40 microg/L), 6-AM (4 microg/L) and cocaine and BE (8 microg/L), yielded 28 opiate- and 50 cocaine-positive specimens. Oral fluid is a promising alternative matrix to monitor opiate and cocaine use in drug testing programs. These data guide interpretation of oral fluid test results and evaluate currently proposed SAMHSA oral fluid testing cutoffs.
Figures
References
-
- Bermejo AM, Lucas ACS, Tabernero MJ. Saliva/plasma ratio of methadone and EDDP. Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 2000;24:70–72. - PubMed
-
- Choo RE, Huestis MA. Oral fluid as a diagnostic tool. Clinical Chemistry Laboratory Medicine. 2004;42:1273–1287. - PubMed
-
- Clauwaert K, Decaestecker T, Mortier K, Lambert W, Deforce D, Van Peteghem C, Van Bocxlaer J. The determination of cocaine, benzoylecgonine, and cocaethylene in small-volume oral fluid samples by liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 2004;28:655–659. - PubMed
-
- Cone EJ. Saliva testing for drugs of abuse. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1993;694:91–127. - PubMed
-
- Cone EJ. Legal, workplace, and treatment drug testing with alternate biological matrices on a global scale. Forensic Science International. 2001;121:7–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

