Phosphorus in prebiotic chemistry
- PMID: 17008215
- PMCID: PMC1664685
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2006.1901
Phosphorus in prebiotic chemistry
Abstract
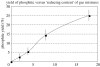
The prebiotic synthesis of phosphorus-containing compounds-such as nucleotides and polynucleotides-would require both a geologically plausible source of the element and pathways for its incorporation into chemical systems on the primitive Earth. The mineral apatite, which is the only significant source of phosphate on Earth, has long been thought to be problematical in this respect due to its low solubility and reactivity. However, in the last decade or so, at least two pathways have been demonstrated which would circumvent these perceived problems. In addition, recent results would seem to suggest an additional, extraterrestrial source of reactive phosphorus. It appears that the 'phosphorus problem' is no longer the stumbling block which it was once thought to be.
Figures
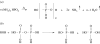

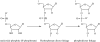
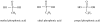
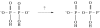
References
-
- Blum H.F. Princeton University Press; Princeton, NJ: 1951. Time's arrow and evolution.
-
- Cooper G.W, Onwo W.M, Cronin J.R. Alkyl phosphonic acids and sulfonic acids in the Murchison meteorite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 1992;56:4109–4115. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(92)90023-C - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Graaf R.M, Schwartz A.W. Reduction and activation of phosphate on the primitive Earth. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2000;30:405–410. doi:10.1023/A:1006700512902 - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Graaf R.M, Schwartz A.W. Thermal synthesis of nucleoside H-phosphonates under mild conditions. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 2005;35:1–10. doi:10.1007/s11084-005-0093-9 - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Graaf R.M, Visscher J, Schwartz A.W. A plausibly prebiotic synthesis of phosphonic aicds. Nature. 1995;378:474–477. doi:10.1038/378474a0 - DOI - PubMed
Additional references
-
- Schwartz A.W. Phosphate: solubilization and activation on the primitive Earth. In: Buvet R, Ponnamperuma C, editors. Chemical evolution and the origin of life. North-Holland; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 1971. pp. 100–108.
-
- Tian F, Toon O.B, Pavlov A.A, De Sterck H. A hydrogen-rich early Earth atmosphere. Science. 2005;308:1014–1017. doi:10.1126/science.1106983 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

