PI3K regulates pleckstrin-2 in T-cell cytoskeletal reorganization
- PMID: 17008542
- PMCID: PMC1785144
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-001339
PI3K regulates pleckstrin-2 in T-cell cytoskeletal reorganization
Abstract
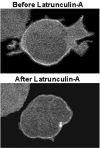
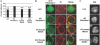
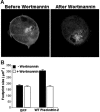
Pleckstrin-2 is composed of 2 pleckstrin homology (PH) domains and a disheveled-Egl-10-pleckstrin (DEP) domain. A lipid-binding assay revealed that pleckstrin-2 binds with greatest affinity to D3 and D5 phosphoinositides. Pleckstrin-2 expressed in Jurkat T cells bound to the cellular membrane and enhanced actin-dependent spreading only after stimulation of the T-cell antigen receptor or the integrin alpha4beta1. A pleckstrin-2 variant containing point mutations in both PH domains failed to associate with the Jurkat membrane and had no effect on spreading under the same conditions. Although still membrane bound, a pleckstrin-2 variant containing point mutations in the DEP domain demonstrated a decreased ability to induce membrane ruffles and spread. Pleckstrin-2 also colocalized with actin at the immune synapse and integrin clusters via its PH domains. Although pleckstrin-2 can bind to purified D3 and D5 phosphoinositides, the intracellular membrane association of pleckstrin-2 and cell spreading are dependent on D3 phosphoinositides, because these effects were disrupted by pharmacologic inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). Our results indicate that pleckstrin-2 uses its modular domains to bind to membrane-associated phosphatidylinositols generated by PI3K, whereby it coordinates with the actin cytoskeleton in lymphocyte spreading and immune synapse formation.
Figures
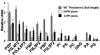



References
-
- Tyers M, Rachubinski RA, Stewart MI, et al. Molecular cloning and expression of the major protein kinase C substrate of platelets. Nature. 1988;333:470–473. - PubMed
-
- Ponting CP, Bork P. Pleckstrin's repeat performance: a novel domain in G-protein signaling? Trends Biochem Sci. 1996;21:245–246. - PubMed
-
- Lemmon MA, Ferguson KM, Schlessinger J. PH domains: diverse sequences with a common fold recruit signaling molecules to the cell surface. Cell. 1996;85:621–624. - PubMed
-
- Abrams CS, Zhao W, Belmonte E, Brass LF. Protein kinase C regulates pleckstrin by phosphorylation of sites adjacent to the N-terminal pleckstrin homology domain. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:23317–23321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

