Aqueous extract of Terminalia arjuna prevents carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic and renal disorders
- PMID: 17010209
- PMCID: PMC1599753
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-6-33
Aqueous extract of Terminalia arjuna prevents carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic and renal disorders
Abstract
Background: Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is a well-known hepatotoxin and exposure to this chemical is known to induce oxidative stress and causes liver injury by the formation of free radicals. Acute and chronic renal damage are also very common pathophysiologic disturbances caused by CCl4. The present study has been conducted to evaluate the protective role of the aqueous extract of the bark of Termnalia arjuna (TA), an important Indian medicinal plant widely used in the preparation of ayurvedic formulations, on CCl4 induced oxidative stress and resultant dysfunction in the livers and kidneys of mice.
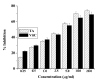
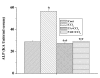
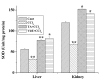
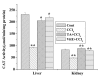
Methods: Animals were pretreated with the aqueous extract of TA (50 mg/kg body weight) for one week and then challenged with CCl4 (1 ml/kg body weight) in liquid paraffin (1:1, v/v) for 2 days. Serum marker enzymes, namely, glutamate pyruvate transaminase (GPT) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) were estimated in the sera of all study groups. Antioxidant status in both the liver and kidney tissues were estimated by determining the activities of the antioxidative enzymes, superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione-S-transferase (GST); as well as by determining the levels of thiobarbutaric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and reduced glutathione (GSH). In addition, free radical scavenging activity of the extract was determined from its DPPH radical quenching ability.
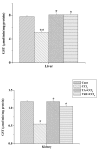
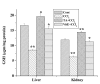
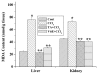
Results: Results showed that CCl4 caused a marked rise in serum levels of GPT and ALP. TBARS level was also increased significantly whereas GSH, SOD, CAT and GST levels were decreased in the liver and kidney tissue homogenates of CCl4 treated mice. Aqueous extract of TA successfully prevented the alterations of these effects in the experimental animals. Data also showed that the extract possessed strong free radical scavenging activity comparable to that of vitamin C.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that the aqueous extract of the bark of TA could protect the liver and kidney tissues against CCl4-induced oxidative stress probably by increasing antioxidative defense activities.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Carbon tetrachloride induced kidney and lung tissue damages and antioxidant activities of the aqueous rhizome extract of Podophyllum hexandrum.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011 Feb 28;11:17. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-11-17. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2011. PMID: 21356055 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo antioxidative and hepatoprotective activity of aqueous extract of Cortex Dictamni.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Apr 28;23(16):2912-2927. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i16.2912. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28522909 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo antioxidant effect of aqueous root bark, stem bark and leaves extracts of Vitex doniana in CCl4 induced liver damage rats.Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2013 May;3(5):395-400. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(13)60083-0. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2013. PMID: 23646304 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity of carbon tetrachloride, free radicals and role of antioxidants.Rev Environ Health. 2020 Sep 25;36(2):279-295. doi: 10.1515/reveh-2020-0048. Print 2021 Jun 25. Rev Environ Health. 2020. PMID: 32970608 Review.
-
Nigella sativa L. and Its Bioactive Constituents as Hepatoprotectant: A Review.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2018;19(1):43-67. doi: 10.2174/1389201019666180427110007. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29701149 Review.
Cited by
-
Mangiferin, a natural xanthone, protects murine liver in Pb(II) induced hepatic damage and cell death via MAP kinase, NF-κB and mitochondria dependent pathways.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56894. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056894. Epub 2013 Feb 25. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23451106 Free PMC article.
-
Terminalia arjuna bark extract alleviates nickel toxicity by suppressing its uptake and modulating antioxidative defence in rice seedlings.Protoplasma. 2016 Nov;253(6):1449-1462. doi: 10.1007/s00709-015-0899-x. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Protoplasma. 2016. PMID: 26497693
-
In vitro inhibition of calcium oxalate crystallization and crystal adherence to renal tubular epithelial cells by Terminalia arjuna.Urolithiasis. 2016 Apr;44(2):117-25. doi: 10.1007/s00240-015-0822-0. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Urolithiasis. 2016. PMID: 26424092
-
Phytomedicinal Role of Pithecellobium dulce against CCl(4)-mediated Hepatic Oxidative Impairments and Necrotic Cell Death.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:832805. doi: 10.1093/ecam/neq065. Epub 2011 Mar 13. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011. PMID: 21869899 Free PMC article.
-
Punica granatum (Pomegranate) Peel Extract Pre-Treatment Alleviates Fenpropathrin-Induced Testicular Injury via Suppression of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Adult Male Rats.Toxics. 2023 Jun 3;11(6):504. doi: 10.3390/toxics11060504. Toxics. 2023. PMID: 37368604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Halliwell B. Oxidative Stress in Dermatology. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York; 1993. Oxygen Species in Pathology with Special Reference to the Skin; pp. 3–11.
-
- Sarkar K, Ghosh A, Kinter M, Mazumder B, Sil PC. Purification and characterization of a 43 kD hepatoprotective protein from the herb Cajanus indicus L. Protein J. 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

