Adeno-associated virus induces apoptosis during coinfection with adenovirus
- PMID: 17011012
- PMCID: PMC1839828
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.08.042
Adeno-associated virus induces apoptosis during coinfection with adenovirus
Abstract
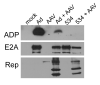
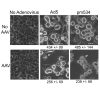
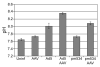
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) is a nonpathogenic parvovirus that efficiently replicates in the presence of adenovirus (Ad). Exogenous expression of the AAV replication proteins induces caspase-dependent apoptosis, but determining if AAV infection causes apoptosis during viral infection is complicated by Ad-mediated programmed cell death. To eliminate Ad-induced cytolysis, we used an E3 adenoviral death protein (ADP) mutant, pm534. AAV and pm534-coinfected cells exhibited increased cell killing compared to pm534 alone. Relative to cells infected with Ad alone, AAV and wild-type Ad-infected cells displayed decreased ADP expression, increased cytolysis until the third day of the infection, and decreased cytolysis thereafter. Biochemical and morphological characteristics of apoptosis were observed during coinfections with AAV and pm534 or Ad, including a moderate degree of caspase activation that was not present during infections with pm534 or Ad alone. AAV coinfection also increased extracellular pH. These studies suggest that AAV induces caspase-dependent and caspase-independent apoptosis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Regulatory Element Near the 3' End of the Adeno-Associated Virus rep Gene Inhibits Adenovirus Replication in cis by Means of p40 Promoter-Associated Short Transcripts.J Virol. 2016 Mar 28;90(8):3981-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03120-15. Print 2016 Apr. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26842470 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of adenovirus E3-11.6K protein induces cell killing by both caspase-dependent and caspase-independent mechanisms.Virology. 2004 Sep 1;326(2):240-9. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2004.06.007. Virology. 2004. PMID: 15302210
-
Recruitment of wild-type and recombinant adeno-associated virus into adenovirus replication centers.J Virol. 1996 Mar;70(3):1845-54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.3.1845-1854.1996. J Virol. 1996. PMID: 8627709 Free PMC article.
-
The Interplay between Adeno-Associated Virus and its Helper Viruses.Viruses. 2020 Jun 19;12(6):662. doi: 10.3390/v12060662. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32575422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helper functions required for wild type and recombinant adeno-associated virus growth.Curr Gene Ther. 2005 Jun;5(3):265-71. doi: 10.2174/1566523054064977. Curr Gene Ther. 2005. PMID: 15975004 Review.
Cited by
-
Adeno-associated virus enhances wild-type and oncolytic adenovirus spread.Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2013 Dec;24(6):372-80. doi: 10.1089/hgtb.2013.124. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2013. PMID: 24020980 Free PMC article.
-
Adeno-associated virus type 2 induces apoptosis in human papillomavirus-infected cell lines but not in normal keratinocytes.J Virol. 2009 Oct;83(19):10286-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00343-09. Epub 2009 Jul 22. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19625406 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of rep-associated factors in herpes simplex virus type 1-induced adeno-associated virus type 2 replication compartments.J Virol. 2010 Sep;84(17):8871-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00725-10. Epub 2010 Jun 23. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20573815 Free PMC article.
-
Parvovirus infection-induced cell death and cell cycle arrest.Future Virol. 2010 Nov;5(6):731-743. doi: 10.2217/fvl.10.56. Future Virol. 2010. PMID: 21331319 Free PMC article.
-
Functional roles of the membrane-associated AAV protein MAAP.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 4;11(1):21698. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01220-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34737404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bantel-Schaal U. Adeno-associated parvoviruses inhibit growth of cells derived from malignant human tumors. Int J Cancer. 1990;45(1):190–4. - PubMed
-
- Casto BC, Armstrong JA, Atchison RW, Hammon WM. Studies on the relationship between adeno-associated virus type 1 (AAV-1) and adenoviruses. II. Inhibition of adenovirus plaques by AAV; its nature and specificity. Virology. 1967;33(3):452–8. - PubMed
-
- Casto BC, Atchison RW, Hammon WM. Studies on the relationship between adeno-associated virus type I (AAV-1) and adenoviruses. I. Replication of AAV-1 in certain cell cultures and its effect on helper adenovirus. Virology. 1967;32(1):52–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM064765-02/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI051471-05/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI51471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM64765/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI051471-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI064129/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM064765-04/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI051471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI64129/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI051471-03/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM064765-03/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM064765/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI051471-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

