Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation
- PMID: 17011499
- PMCID: PMC1958996
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.07.001
Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation
Abstract
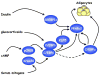
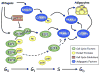
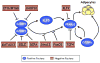
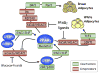
A detailed understanding of the processes governing adipose tissue formation will be instrumental in combating the obesity epidemic. Much progress has been made in the last two decades in defining transcriptional events controlling the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes. A complex network of transcription factors and cell-cycle regulators, in concert with specific transcriptional coactivators and corepressors, respond to extracellular stimuli to activate or repress adipocyte differentiation. This review summarizes advances in this field, which constitute a framework for potential antiobesity strategies.
Figures
References
-
- Arango NA, Szotek PP, Manganaro TF, Oliva E, Donahoe PK, Teixeira J. Conditional deletion of beta-catenin in the mesenchyme of the developing mouse uterus results in a switch to adipogenesis in the myometrium. Dev Biol. 2005;288:276–283. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee SS, Feinberg MW, Watanabe M, Gray S, Haspel RL, Denkinger DJ, Kawahara R, Hauner H, Jain MK. The Kruppel-like factor KLF2 inhibits peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma expression and adipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:2581–2584. - PubMed
-
- Barak Y, Nelson MC, Ong ES, Jones YZ, Ruiz-Lozano P, Chien KR, Koder A, Evans RM. PPAR gamma is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol Cell. 1999;4:585–595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

